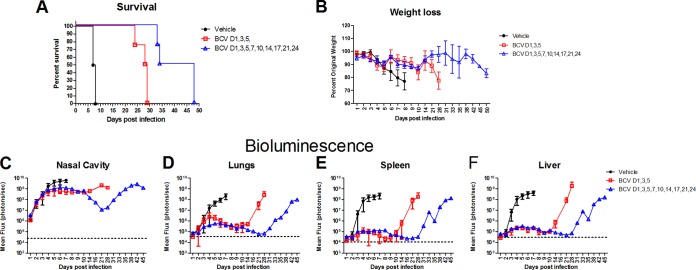
FIG 4.
Treatment with BCV extended survival of nude mice following lethal challenge with IHD-J-Luc VACV. BALB/c nu/nu mice were infected with 104 PFU of IHD-J-Luc VACV and treated with vehicle or 20 mg/kg BCV on days 1, 3, and 5 or on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14, 17, 21, and 24, as indicated. Mice were observed for mortality (A) and weight loss (B) and were imaged daily for the first 10 days and then twice weekly for 45 days to calculate mean fluxes ± SD in the nasal cavity, lungs, spleen, and liver. Mean background levels of fluxes (photons/s) ± SD were recorded in nude mice prior to infection: nasal cavity, 23.3 × 103 ± 4.5 × 103; lungs, 36.3 × 103 ± 11.6 × 103; spleen, 10.9 × 103 ± 2.5 × 103; liver, 30.2 × 103 ± 2.1 × 103. Values are represented as dotted horizontal lines (means only) in panels C to F. Four mice per group were used in the experiment. Short and extended treatment with BCV significantly increased median survival time compared with vehicle-treated mice (P = 0.0025 and P = 0.0091, respectively). The experiment was performed twice with similar results.