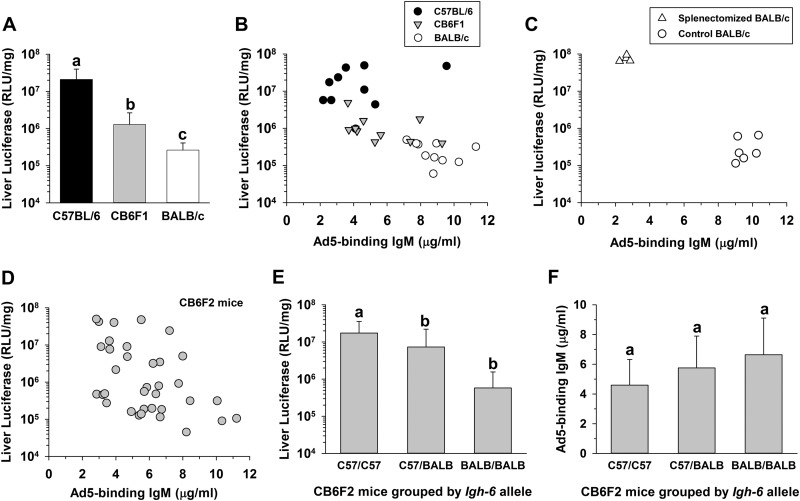
FIG 2.
Influence of mouse strain on IgM concentration and liver transduction. C57BL/6, BALB/c, or hybrid mice were pre-bled to determine serum IgM concentrations and then injected i.v. with 4 × 1011 vp/kg of AdCMV-Luc. Liver transduction was assayed at 48 h. (A) Liver transduction in C57BL/6, BALB/c, and F1 hybrid (CB6F1) mice (n = 10 per group). Groups that do not share the same letter (a, b, and so on) are significantly different from each other (P ≤ 0.05; ANOVA and Holm-Sidak post hoc test). Error bars represent SD. (B) Negative correlation between serum Ad5-binding IgM concentration and liver transduction in individual mice (n = 30, rs = −0.683, P = 0.0000194; Spearman's rank correlation). (C) Effect of splenectomy on Ad5-binding IgM concentration and liver transduction in BALB/c mice (n = 4 or 6). The splenectomized and control (sham surgery) groups differed significantly from each other for both Ad5-binding IgM and luciferase expression (P ≤ 0.000001; t tests). Surgery was performed 2 weeks before injection of vector. (D) Negative correlation between serum IgM concentration and liver transduction in CB6F2 (CB6F1 × CB6F1) mice (n = 35, rs = −0.451, P = 0.00682; Spearman's rank correlation). (E) Dependence of liver transduction on Igh-6 alleles in the same set of 35 CB6F2 mice. Mice having only C57BL/6 Igh-6 alleles showed significantly higher liver transduction than mice that had at least one allele of BALB/c origin (n = 7 to 19 per group, P ≤ 0.05; ANOVA and Holm-Sidak post hoc test). The IgM allotypes in serum from each CB6F2 mouse were determined by ELISA, using allotype-specific anti-IgM clones AF6-78 and MA-69 (BioLegend) to identify BALB/c and C57BL/6 IgM (26, 27). (F) No significant relationship between Igh-6 and Ad5-binding IgM concentration in CB6F2 mice (n = 7 to 19 per group, P = 0.777; ANOVA).