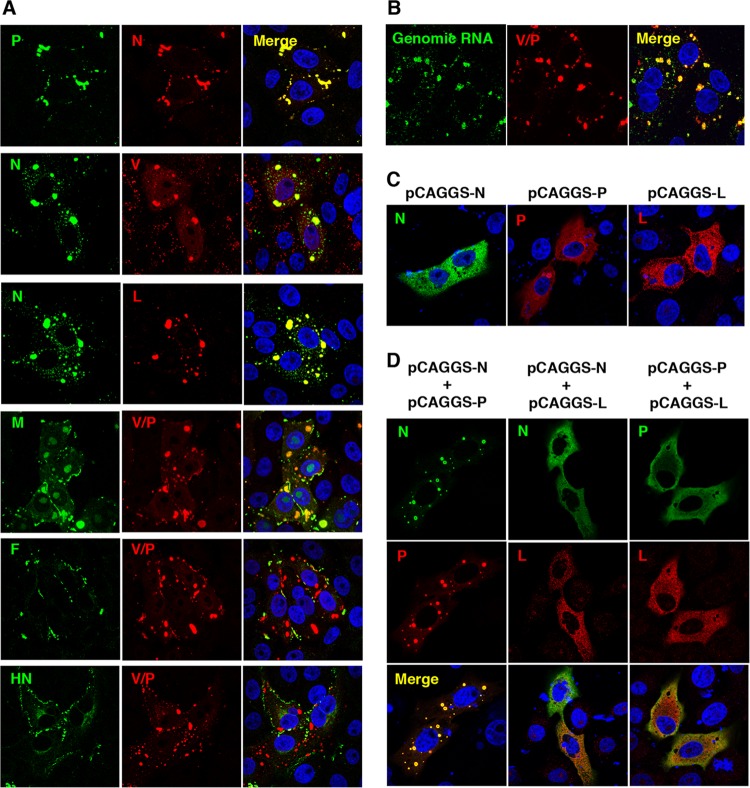
FIG 1.
Intracellular localizations of MuV proteins and genomic RNA. (A) Vero cells infected with MuV were immunostained at 24 h postinfection (p.i.) with mouse anti-N (23D), anti-P (57A), anti-M (79D), anti-F (170C), or anti-HN (78) MAb and rabbit anti-N, anti-V/P (T61), anti-V (T60), or anti-L (L17) PAb, followed by AF488-conjugated anti-mouse IgG and AF594-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG, respectively. The cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) Vero cells infected with MuV were immunostained at 24 h p.i. with rabbit anti-V/P PAb and AF594-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG. Then, the cells were subjected to a fluorescence in situ hybridization assay to detect viral genomic RNA. The cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (C and D) Vero cells transfected with pCAGGS-N, -P, and/or -L alone or in combination were immunostained at 24 h posttransfection with anti-N or anti-P MAb and anti-V/P or anti-L PAb, followed by AF488-conjugated anti-mouse IgG and AF594-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG, respectively. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).