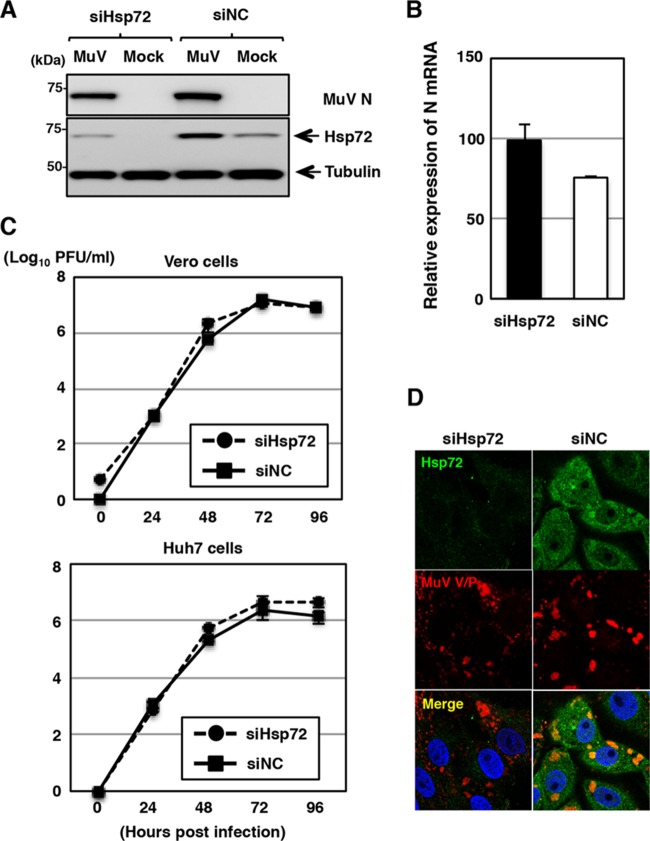
FIG 5.
Effects of Hsp72 knockdown on MuV propagation. (A) At 48 h posttransfection with either siHsp72 or siNC, Vero cells were inoculated with MuV at an MOI of 1.0. The cell lysates were collected at 24 h p.i. and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) At 48 h posttransfection with either siHsp72 or siNC, Vero cells were inoculated with MuV at an MOI of 5.0. Total cellular RNA was extracted at 24 h p.i. and subjected to RT using an oligo(dT) primer. The levels of N mRNA were determined by real-time PCR and calculated as percentages of the control HPRT1 mRNA level. The data are representative of three independent experiments. The error bars indicate the standard deviations of the means. (C) At 48 h posttransfection with either siHsp72 or siNC, Vero or Huh7 cells were infected with MuV at an MOI of 0.01. The supernatants were collected at 24, 48, 72, and 96 h p.i., and the infectious titers were determined by plaque assay in Vero cells. The results shown are from three independent experiments, with the error bars representing the standard deviations. (D) At 48 h posttransfection with either siHsp72 or siNC, Vero cells were inoculated with MuV at an MOI of 1.0. At 24 h p.i., the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and immunostained with mouse anti-Hsp72 MAb and rabbit anti-V/P PAb, followed by AF488-conjugated anti-mouse IgG and AF594-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG. The cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).