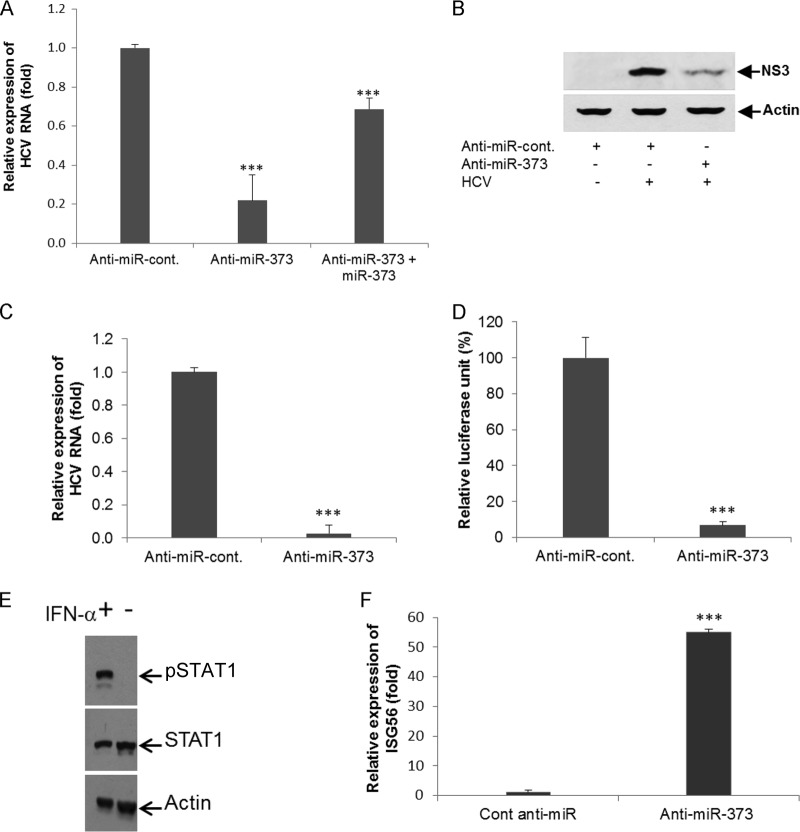
FIG 6.
Knockdown of miR-373 suppresses HCV replication. (A) IHHs were infected with HCV genotype 2a, followed by transfection with anti-control-miR or anti-miR-373. RNA was isolated, and HCV RNA replication was measured by qRT-PCR after 48 h of transfection. For the reciprocal experiment, anti-miR-373-treated HCV-infected IHH were transfected with miR-373, and expression of HCV RNA was measured by qRT-PCR. (B) Hepatocytes were mock treated or infected with HCV genotype 2a, followed by transfection with anti-control-miR or anti-miR-373 after 24 h of infection. Cell lysates were prepared after 96 h postinfection, and HCV NS3 expression levels were analyzed by Western blotting using specific antibodies. The blot was reprobed with an antibody to actin for normalization. (C) Rep2a-Rluc cells were transfected with anti-control-miR or anti-miR-373. HCV genomic RNA replication was analyzed by qRT-PCR after 48 h of transfection. Cellular 18S RNA was used as an internal control for normalization. (D) Rep2a-Rluc cells were transfected with anti-control-miR or anti-miR-373, and relative luciferase activity was measured by a Renilla luciferase assay after 48 h of transfection. Results are presented as the means and standard deviations from three independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001. (E) Huh7.5 cells were treated with IFN-α for 2 h, and cell lysates were analyzed for pSTAT1 and STAT1 expression using specific antibodies. The blot was reprobed with actin for comparison of protein loads. (F) Rep2a-Rluc cells were transfected with anti-control-miR or anti-miR-373 for 48 h, and RNA was extracted for determination of the expression of ISG56 by qRT-PCR. 18S RNA was used for normalization. Results are presented as the means and standard deviations from three independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001.