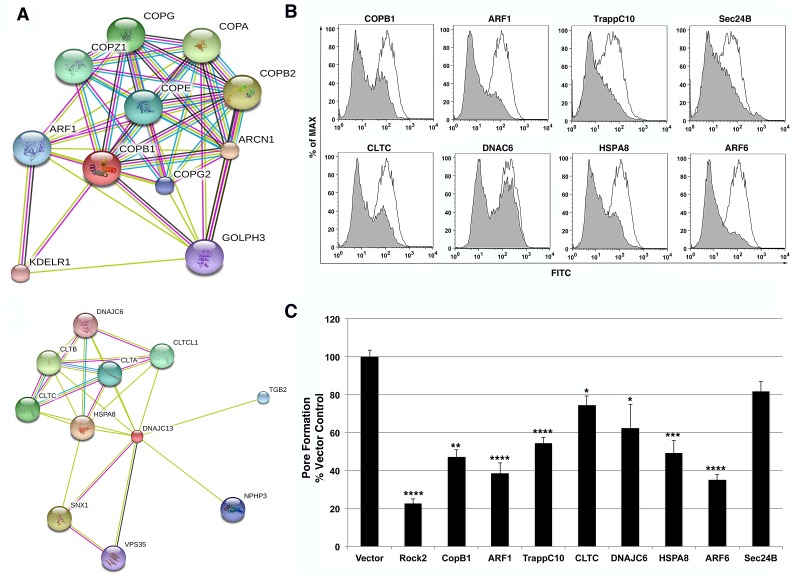
FIG 4 .
Intracellular protein trafficking pathways that support the function of the YopB/D translocon. (A) String analysis of COPB1 and CLTC allows identification of functional partners in each respective pathway. (B and C) Intracellular protein trafficking shRNAs were assessed in YopB/D functional assay. 293T cells were transfected with individual shRNA plasmids coexpressing mCherry. After 72 h of knockdown, cells were incubated with Y. pseudotuberculosis YPIII ΔyopHMOJE for 2 h at an MOI of 25. All cells were then stained using a FITC LIVE/DEAD cell viability kit (Invitrogen) for 30 min at RT and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Representative histograms depicting FITC fluorescence of mCherry+ cells are displayed as overlays for each labeled shRNA (gray) compared to vector control (white). (C) YopB/D pore formation was quantitated as the MFI of FITC for mCherry+ cells normalized to the vector control. Each shRNA was evaluated in this assay in triplicate in a minimum of three independent experiments. Data represented as means plus standard errors of the means (SEM) (error bars) for all experiments. Statistical significance was determined using an ANOVA (P < 0.0001) with Dunnett’s posthoc test. Values that are significantly different from the value for the vector control are indicated by asterisks as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.