FIG 7 .
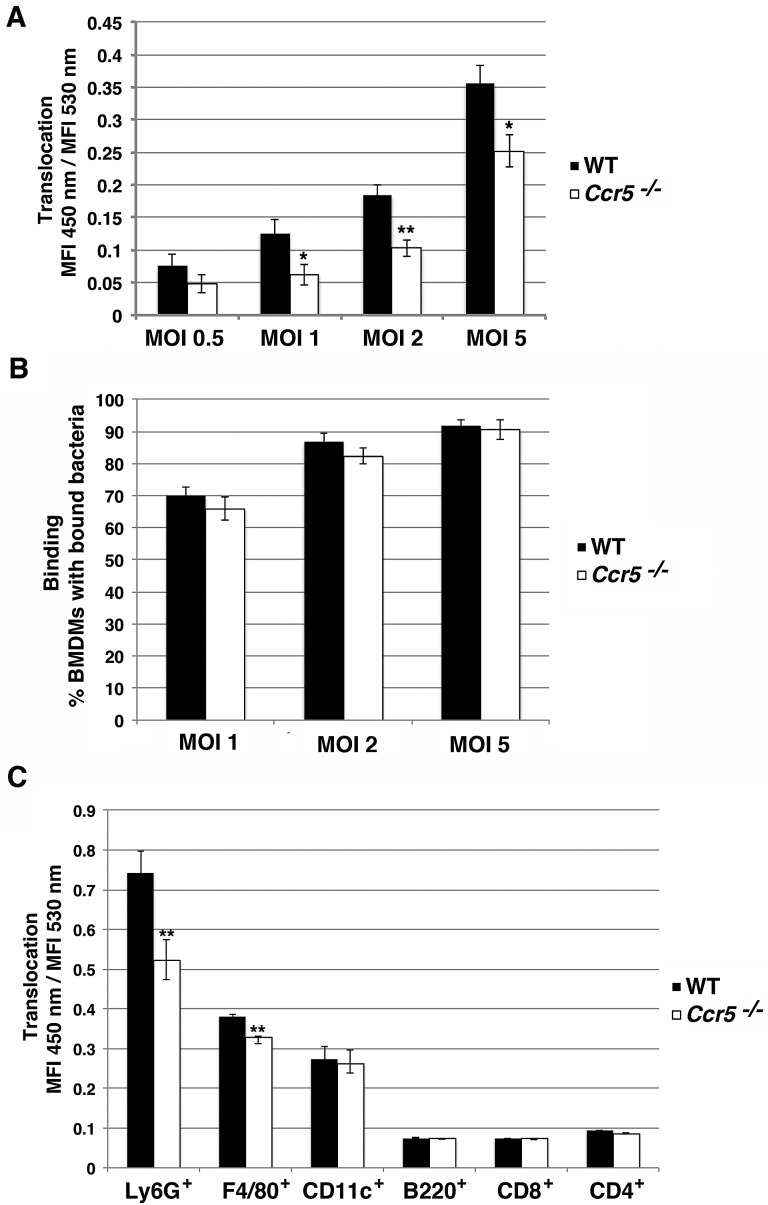
Primary immune cells from Ccr5−/− mice have defect in YopE-TEM translocation. (A) YopE-TEM translocation is attenuated in Ccr5−/− macrophages. Primary BMDMs from wild-type and Ccr5−/− C57BL/6 mice were challenged with Y. pseudotuberculosis YPIII YopE-TEM strain at the indicated MOI for 1 h at 37°C. The cells were then loaded with CCF2-AM for 30 min at RT, lifted, and analyzed on a BD LSRII flow cytometer. Translocation was measured at the MFI 450-nm emission/MFI 530-nm emission after 405-nm excitation. (B) Bacteria bind efficiently to both WT and Ccr5−/− macrophages. BMDMs were incubated with Y. pseudotuberculosis YPIII gfp+ at the indicated MOI for 15 min at 37°C, washed, fixed, and stained with Hoechst. Binding was determined by counting macrophages with GFP+ bound bacteria using fluorescence microscopy. (C) Translocation of YopE-TEM is attenuated in splenic neutrophils. Splenocytes harvested from wild-type and Ccr5−/− C57BL/6 mice were incubated with YPIII strain expressing YopE-TEM at an MOI of 0.5 for 45 min at 37°C. The cells were then treated with gentamicin, loaded with a CCF2-AM solution for 30 min at RT, followed by surface staining to the indicated surface markers and analysis by flow cytometry. Translocation was measured for individual cell types by measuring the MFI of 450-nm emission/MFI of 530-nm emission after 405-nm excitation within each gated population. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated a minimum of three times. Data are means ± SEM for all experiments. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired two tailed t test assuming unequal variances (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).