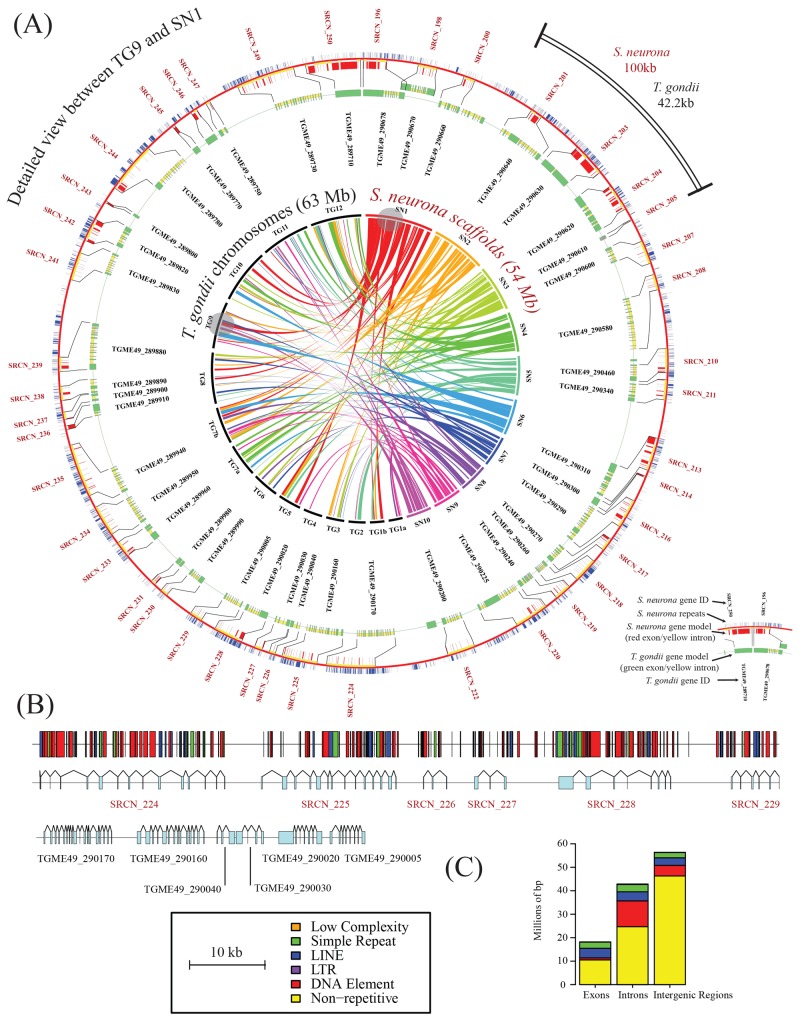
FIG 1 .
Architecture and syntenic relationships of the S. neurona genome. (A) Circos representations (50) of syntenic relationships between the genomes of S. neurona and T. gondii ME49. The inner circle shows syntenic relationships among the 10 largest S. neurona genomic scaffolds (maximum size, 9.2 Mb; minimum size, 3.5 Mb) and the 14 chromosomes of T. gondii. Bandwidths indicate alignment length, and colors represent the S. neurona scaffold of origin for the gene clusters. Grey circles indicate the largest regions of genomic synteny between S. neurona scaffold SO SN1 and T. gondii chromosome 9. The outer circles show a detailed view of synteny indicated by the grey circles. Red and green bars indicate exons of S. neurona and T. gondii, respectively, and yellow and blue bars indicate intronic and repeat regions, respectively. (B) Detailed view of the synteny map shown in panel A revealing larger introns in S. neurona relative to those in T. gondii and the relative positioning of repetitive elements. (C) Incidence of repeats in different genomic regions as defined by RepeatModeler (20).