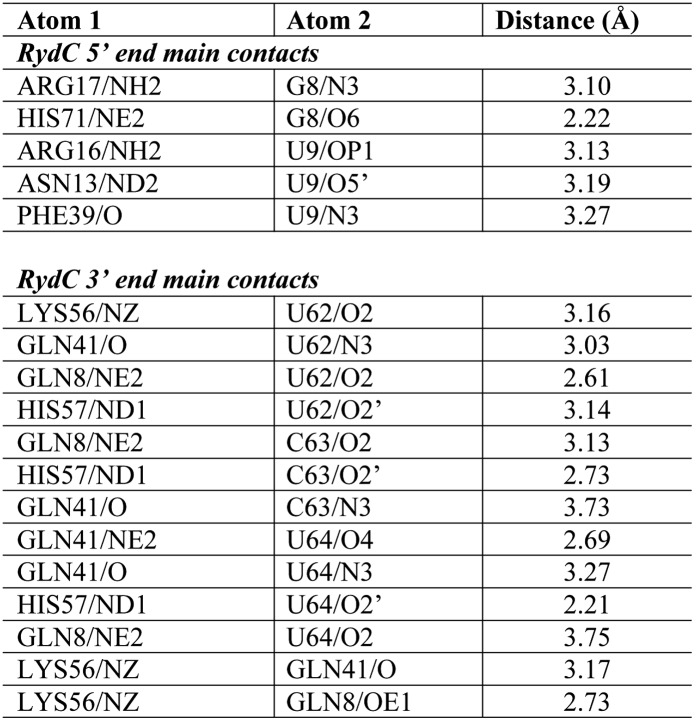
Figure 3. Interactions established by the 3′-end and 5′-end regions of RydC with two adjacent Hfq hexamers in the crystal lattice.
(A) RydC is sandwiched between two Hfq hexamers in the crystal lattice. Two asymmetric units are shown with the RydC in the centre (coloured in orange) bridging two Hfq hexamers. The symmetry-related Hfq molecule is labelled with an asterisk (*). The 3′-end region of RydC in the main asymmetric unit is pointed by an arrow and contacts the proximal face of the principal Hfq hexamer, another arrow indicates the position of the 5′-end of RydC, interacting with a portion of the rim of the Hfq hexamer in the neighbouring asymmetric unit. Two black rectangles define the 5′-end and 3′-end RydC–Hfq contact regions, which are enlarged in panels B and C respectively. (B) Contacts established between the 5′-end seed region of RydC and the rim of a symmetry related Hfq molecule. The main interactions at this interface involve the following amino acid–nucleotide pairs: R17-G8, H71-G8, R16-U9, N13-U9, F39-U9, Q5-G11, P10-A10. Residues belonging to the symmetry related Hfq molecules are labelled with an asterisk (*). (C) Interactions of the poly-U 3′-end of RydC with the recessed groove of the proximal face of Hfq. The uridines and cytosine stack on F42; this and other interactions are similar to those seen in the U6/Hfq crystal structure (Sauer and Weichenrieder, 2011). The side chains of critical residues that contribute to keep RydC in the channel are shown in stick representation. The adjacent protomers of Hfq are coloured in blue and cyan, RydC is shown in orange. Side chains are shown for all residues, main chains are shown for Q41 in order to highlight the position of atoms involved in interactions with neighbouring residues. The RNA used in the crystallisations has a guanine on the 3′-end originating from the template for in vitro transcription, but this base may be in multiple conformations.