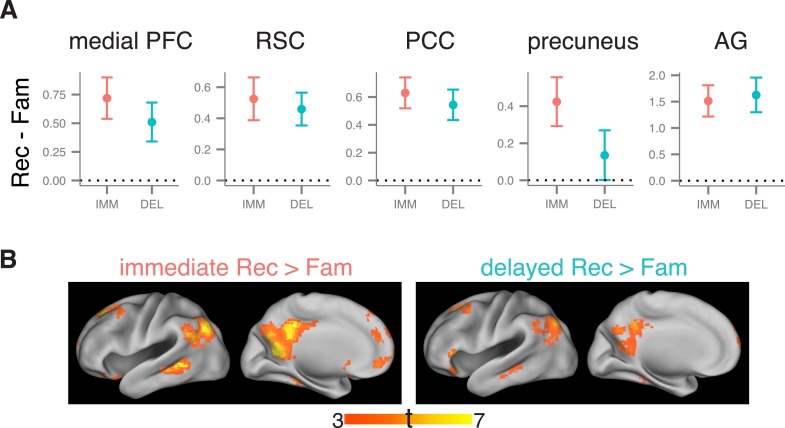
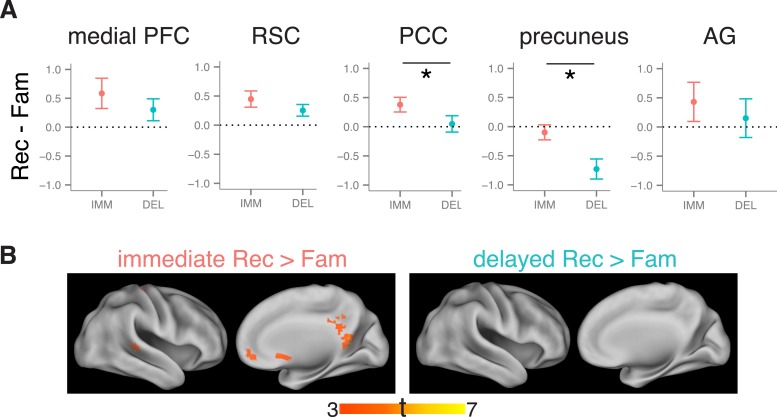
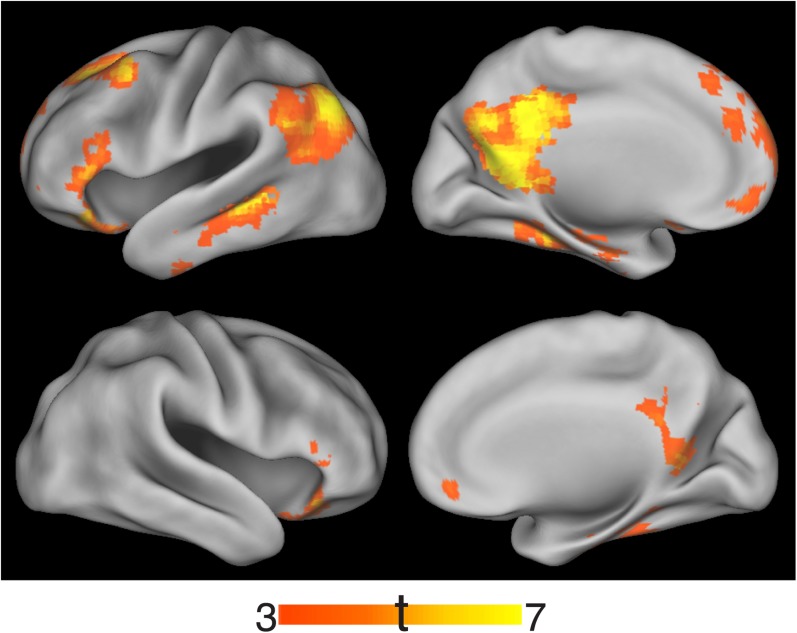
Figure 3. Recollection-related activity in the cortical recollection network.
(A) Univariate estimates of recollection-related activity, that is, the difference in activation for recollection and familiarity trials, for cortical ROIs in the recollection network. Results for left-hemisphere ROIs are shown (see Figure 3—figure supplement 1 for right-hemisphere ROIs). Error bars denote the standard error of the mean. Note that although the precuneus appears to show a reduction in recollection-related activity over time, the interaction was not significant. Summary statistics for individual subjects are contained in Figure 3—source data 1. (B) Voxel-wise maps of recollection-related activity, that is, the difference between recollection and familiarity trial activity, thresholded to display significant clusters (voxel-wise p < 0.001, cluster-corrected p < 0.05). Maps are displayed separately for immediate and delayed recollection. Surface images were rendered in Caret using the PALS atlas (left hemisphere shown; see Figure 3—figure supplement 1 for right hemisphere). Peaks are reported in Supplementary file 2. The conjunction of immediate and delayed recollection-related activity is shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05025.010