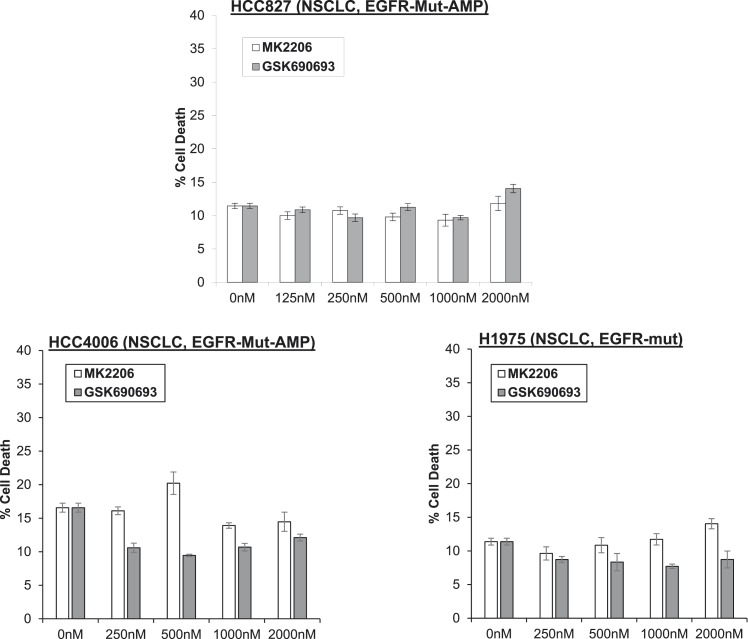
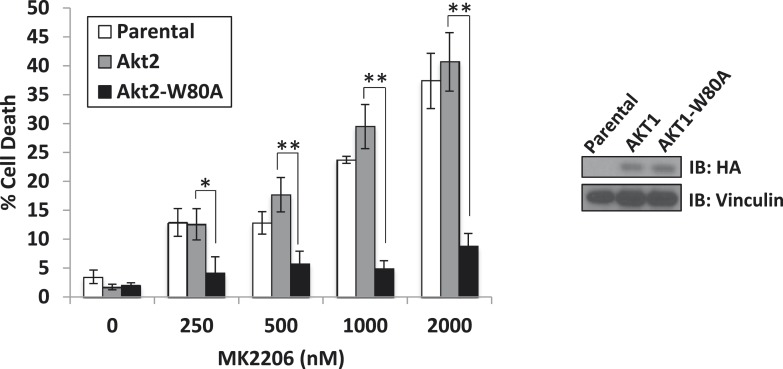
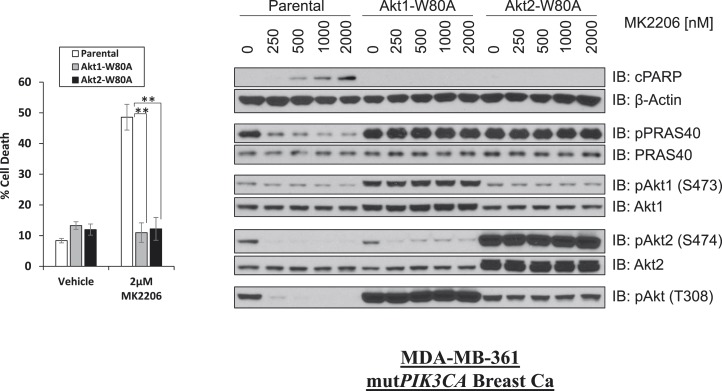
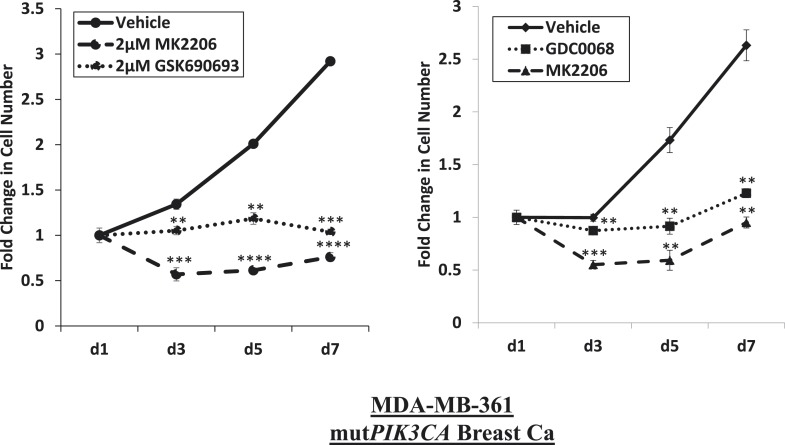
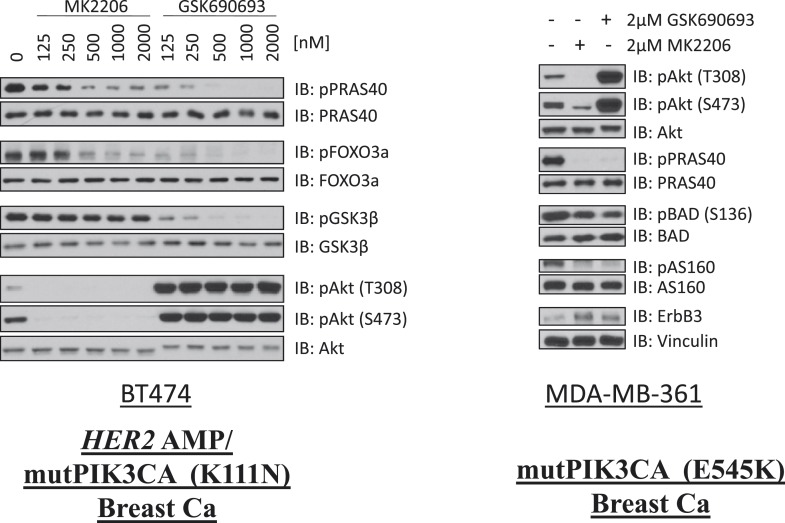
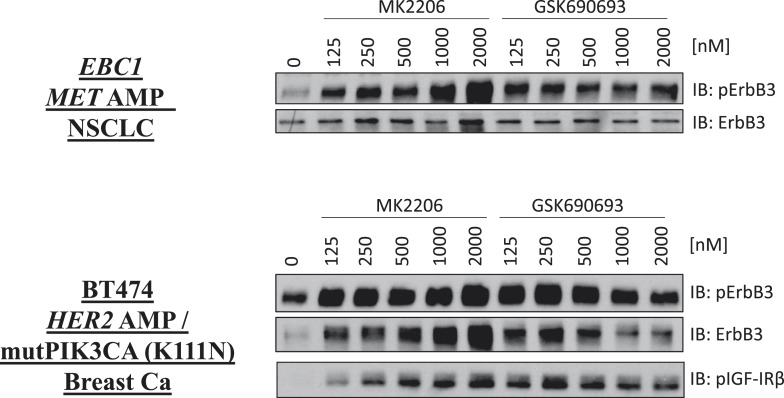
Figure 1. Differential sensitivity of human cancer cells to different classes of AKT inhibitors.
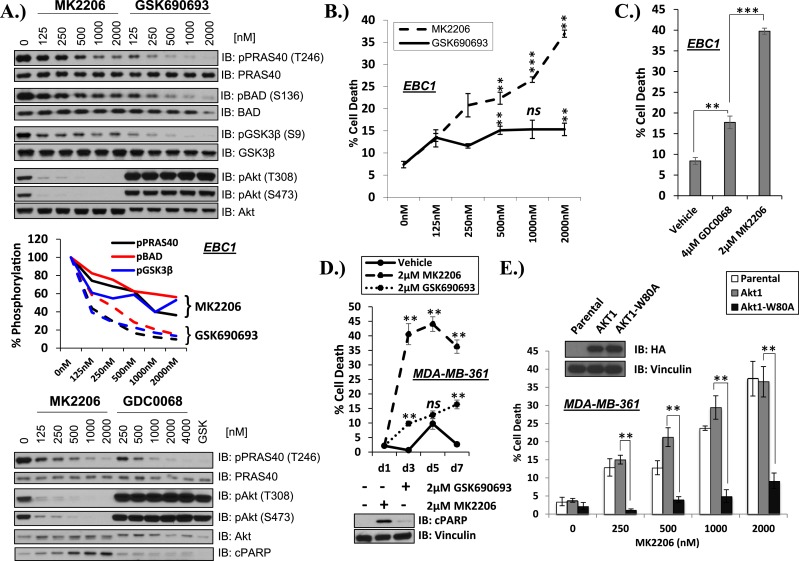
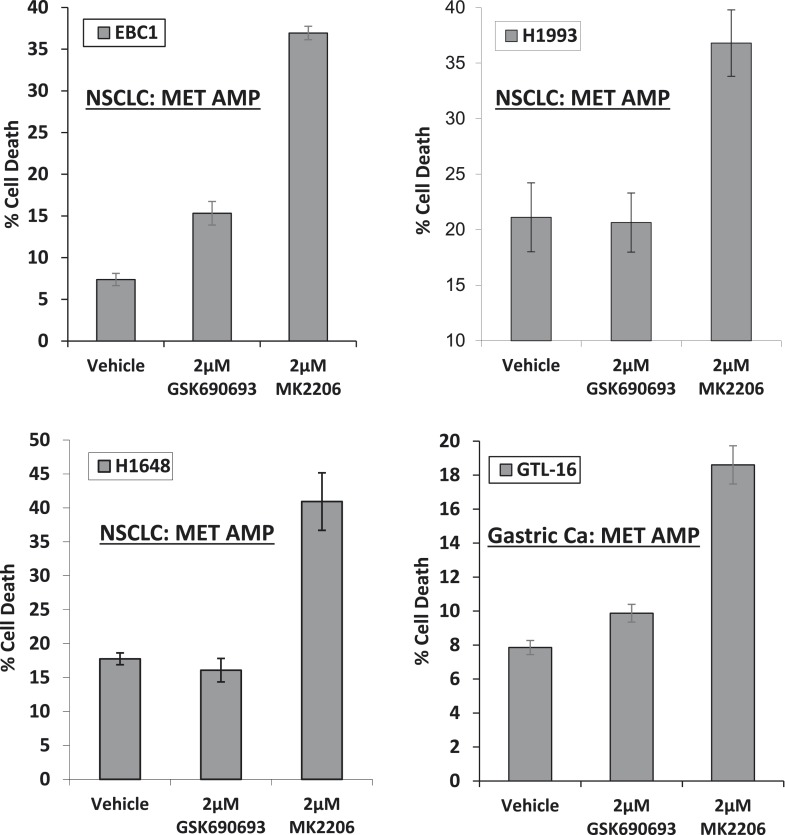
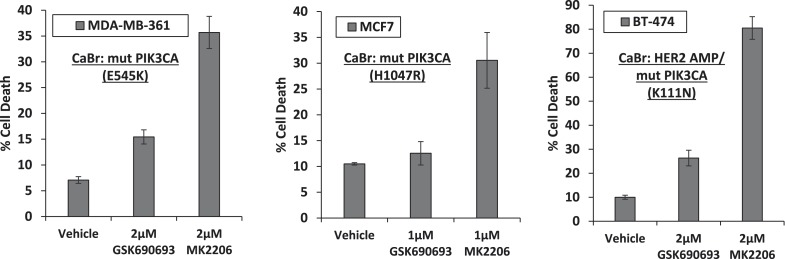
(A) Effect of AKT inhibitors on phosphorylation of AKT and AKT protein substrates. EBC1 cells were treated with the indicated doses of MK2206 and GSK690693 (top), or GDC0068 (bottom) for 24 hr. Treated cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblot with the indicated antibodies. Phosphorylation of PRAS40, BAD, and GSK3β was quantified by image densitometry (middle). (B) Allosteric AKT inhibitor MK2206 induces more cell death than ATP-competitive inhibitor GSK690693 in EBC1 human lung cancer cells. Cells were treated with drug or vehicle for 96 hr. Cell death was determined by the trypan blue method. Error bars denote standard error of the mean (t-test *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, treatment vs vehicle). (C) Allosteric AKT inhibitor MK2206 induces more cell death than ATP-competitive inhibitor GDC0068. Experimental conditions were as in Figure 1B. (D) Allosteric AKT inhibitor MK2206 induces more cell death than the ATP-competitive inhibitor GSK690693 in MDA-MB-361 human breast cancer cells. Cell death was assessed on day 1, day 3, day 5, and day 7 following treatment with vehicle or 2 µM of MK2206 or 2 µM of GSK690693(top) (t-test *p ≤ 0.05,**p ≤ 0.01, treatment vs vehicle). An additional plate from each treatment group was lysed 24 hr after drug treatment and analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies (bottom). (E) Suppression of MK2206-induced cell death by a drug-resistant allele of AKT1. MDA-MB-361 cells were stably transduced with HA-tagged wild-type AKT1 or AKT1-W80A and treated with 2 µM MK2206 for 96 hr. Cell death was assessed as above. Expression of the transgenes was confirmed by immunoblot using an HA antibody, and loading was controlled with a vinculin antibody (inset).
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03751.003
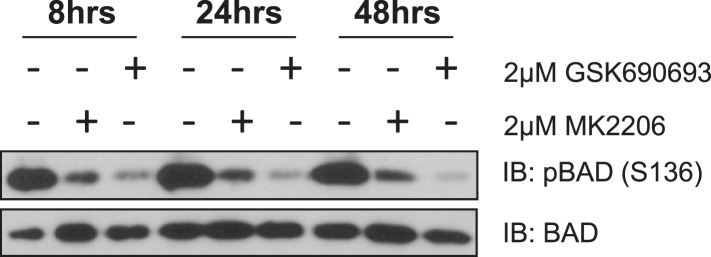
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. MK2206 and GSK690693 cause sustained suppression of AKT-dependent BAD phosphorylation.