Fig 3.
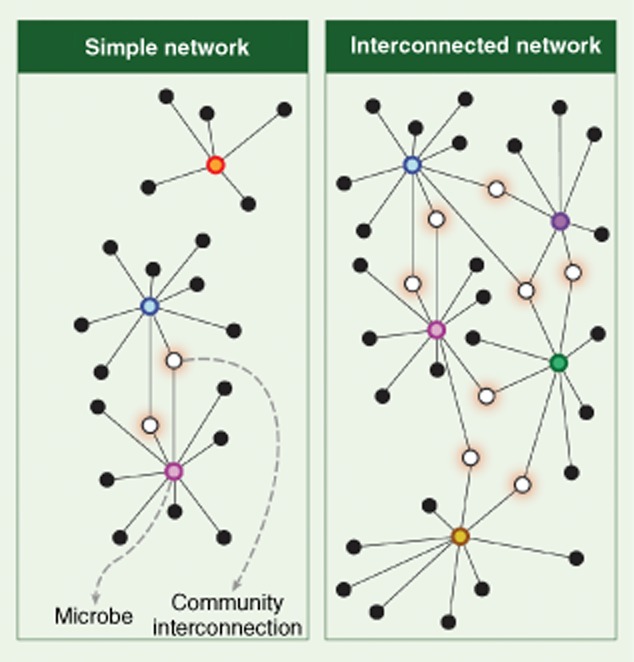
Functional networks link the function of microbes and support community stability and resilience. Functional networks in the gut are extensive and imply that targeted modulation of the gut microbiota may have unexpected impact on the viability of off-target species. Left: low interconnectivity may render gut communities prone to change as the result of relatively small perturbation. Right: highly interconnected networks may be more robust and resistant to change.
