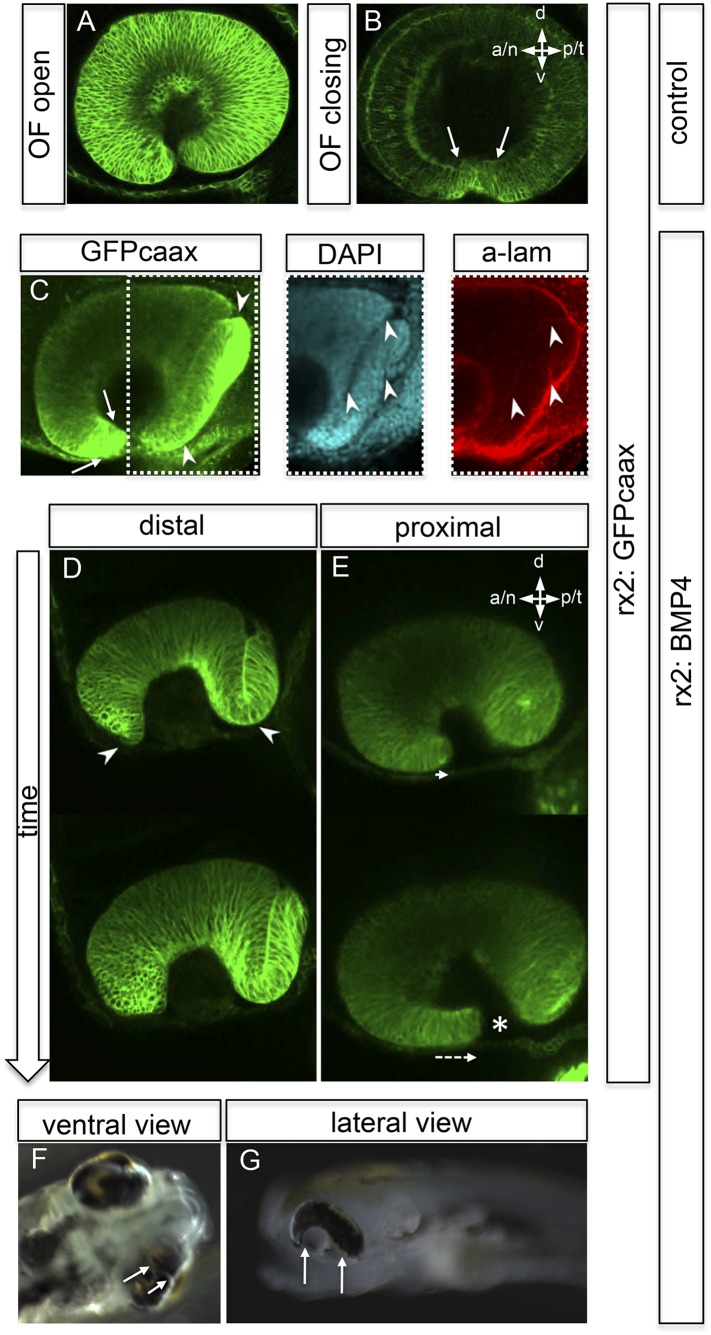
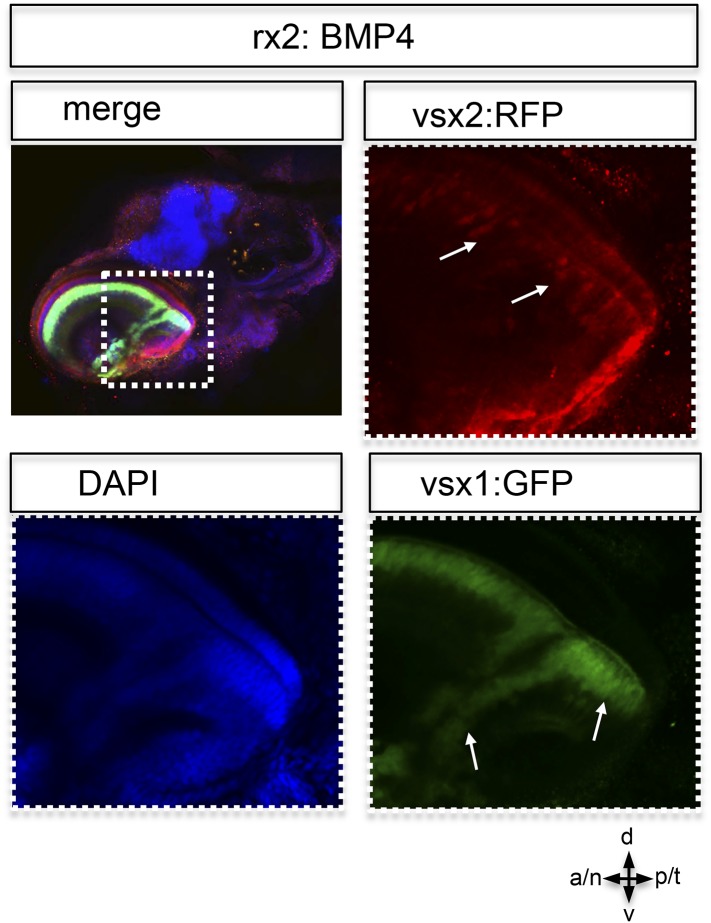
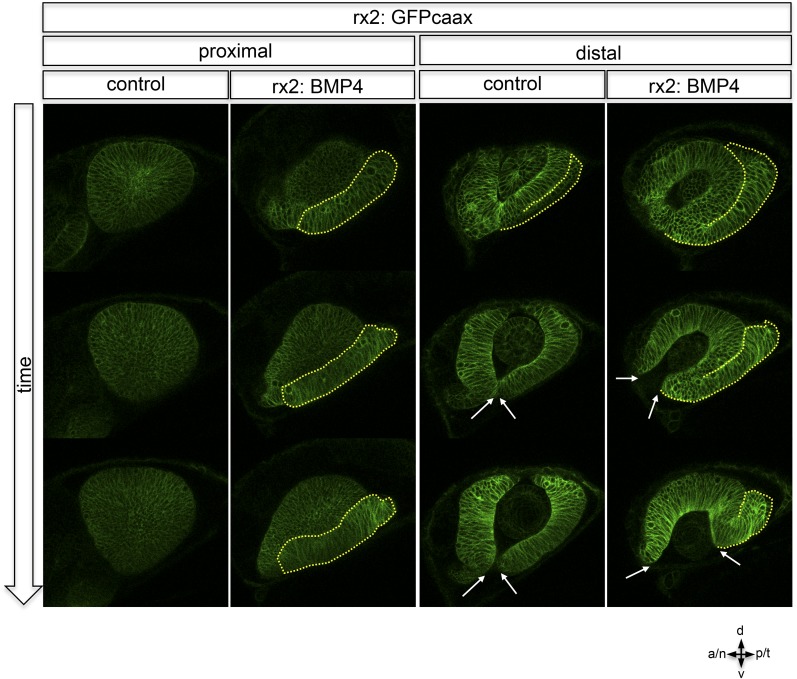
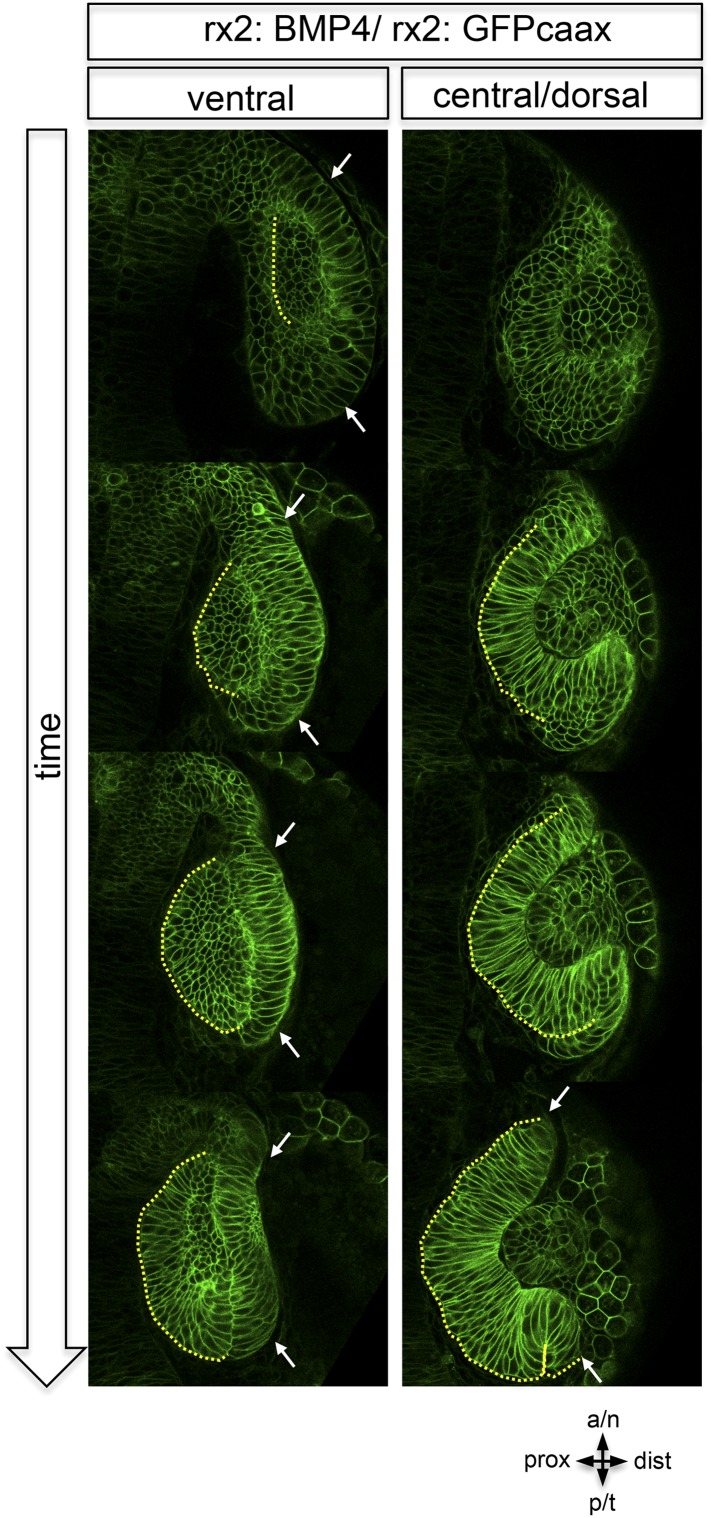
Figure 6. Impaired eye gastrulation results in coloboma.
(A–B) Membrane-localized GFP (rx2::GFPcaax) in a developing eye during optic fissure closure (A = early, B = late) (lateral view, derived from imaging data, (A) start at 24 hpf, (B) after 34 hr imaging at 22°C). Rx2 is expressed in retinal stem cells/RPCs (A) and after NR differentiation is additionally expressed in photoreceptors and Müller Glia (B) while its expression is maintained in retinal stem cells of the CMZ (Reinhardt and Centanin et al., submitted). The optic fissure margins are still undifferentiated (arrows in B), (C) developing eye of rx2::BMP4 fish (lateral view), membrane-localized GFP (rx2::GFPcaax, anti-GFP immunointensified), DAPI nuclear labeling and anti-laminin immunostaining, the optic fissure is visible, noteworthy the temporal retina is mis-shaped and folded into the RPE domain (best visible in DAPI, arrowheads), and located on a basal membrane (arrowheads in anti-laminin), especially the temporal optic fissure margin (arrowheads in GFPcaax) is located in the folded part of the temporal retina and not facing the optic fissure (arrows in GFPcaax) (24 hpf) (D–E) impaired optic fissure closure in rx2::BMP4 embryos over time at a proximal (E) and a distal (D) level. (Data obtained from 4D imaging of rx2 ::BMP4/ rx2::GFPcaax started at 21.5 hr. Data are also presented as Video 10.) Importantly, next to the affected temporal optic cup also the nasal optic cup is mis-folded (arrowheads in D). Remarkably, however, the nasal optic fissure margin extents into the optic fissure (dashed arrow in E) but the temporal optic fissure margin does not, likely being the result of the intense mis-bending of the temporal optic cup. This results in a remaining optic fissure (asterisk in E). (F–G) Brightfield images of variable phenotype intensities observed in rx2::BMP4 hatchlings.