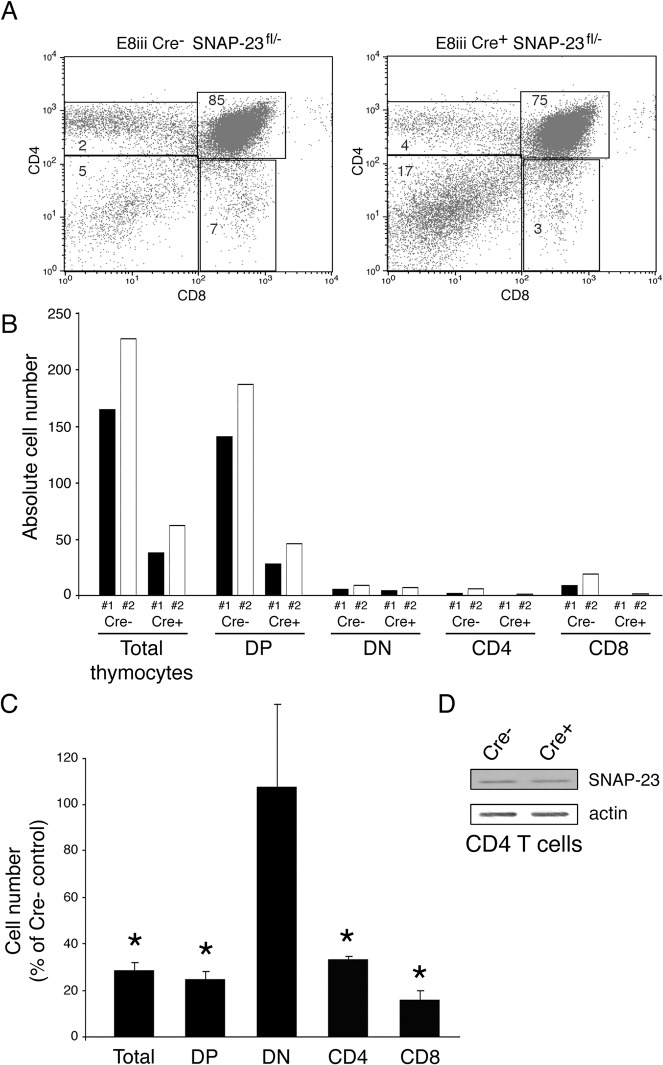
Fig 4. Deletion of SNAP-23 in CD4+CD8+ T cells prevents T cell development.
Thymi were harvested from E8iii-Cre- SNAP-23fl/- control mice or E8iii-Cre+ SNAP-23fl/- mice (line E3) and single cell suspensions were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated CD4- and CD8-mAb and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) A representative flow cytometry profile reveals a dramatic reduction in the percentage of CD4+, CD4+8+, and CD8+ T cells in the thymus of an E8iii-Cre+-expressing SNAP-23fl/- mouse. (B) Quantitative analysis of matched pairs of Cre- and Cre+ SNAP-23fl/- littermate mice lines indicate recovery of CD4-CD8- (DN), CD4+CD8+ (DP), CD4+, and CD8+ T cells present in thymi of E8iii-Cre+ SNAP-23fl/- mice expressed as a percentage of those found in thymi of E8iii-Cre- SNAP-23fl/- control mice (calculated based on the percentage of each cell type present as determined by flow cytometry). (C) The recovery of the indicated cell types from the thymi of E8iii-Cre+ SNAP-23fl/- mice was expressed as a percentage of those found in E8iii-Cre- SNAP-23fl/- control mouse spleens. The data shown are mean +/- SD of five independent experiments (*p<0.05). (D) CD4 T cells were purified from the thymi from the indicated mice and equal numbers of cell equivalents were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using a SNAP-23 antibody. The blot was re-probed for anti-β actin mAb as a loading control.