Abstract
To expand the electron microscopist's options in localization and visualization, a new and general staining technique has been tested. The avidin-biotin complex serves as a coupling between the electron-dense marker, ferritin, and points of interest in biological samples. When specific cellular components are tagged with biotin, those components may be visualized with ferritin-linked avidin. Because of the remarkably strong affinity of avidin and biotin (characterized by an association constant of 1015 M-1), the staining is rapid and stable.
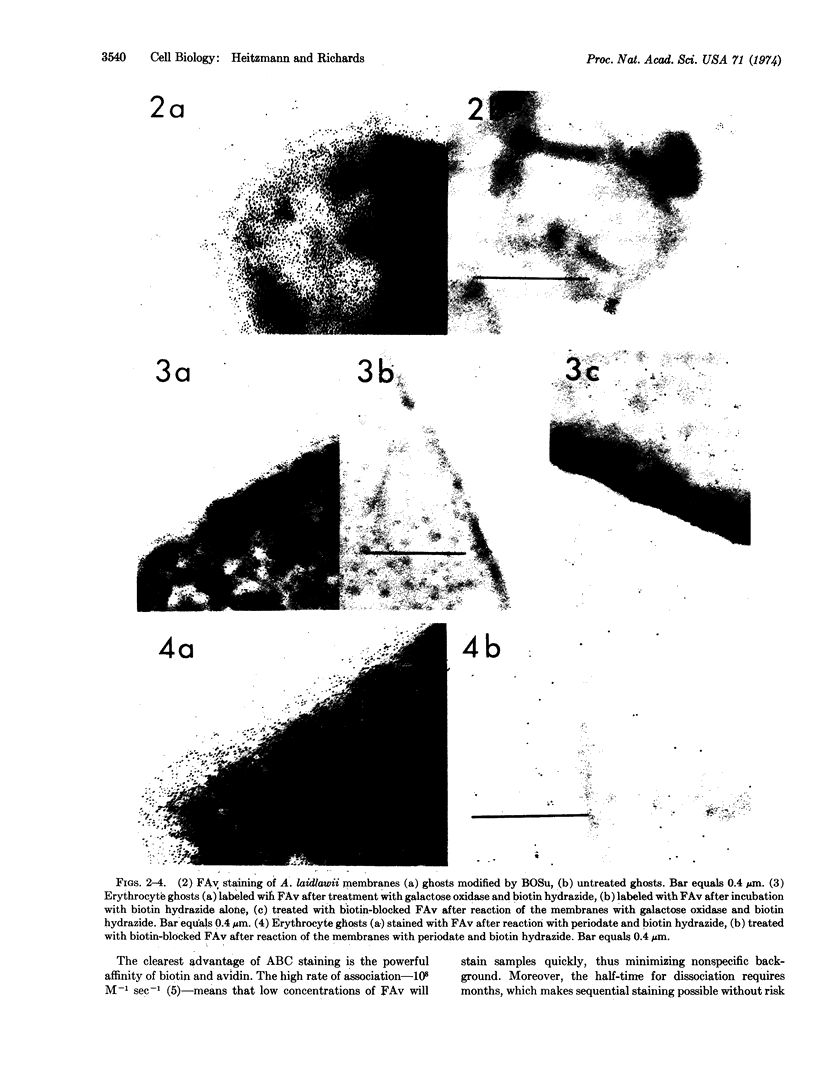
The preparation of ferritin-avidin conjugate is described, and examples are presented of the application of this complex to biotin-tagged membranes. The ghosts of Acholeplasma laidlawii have been treated with biotinyl-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester to label protein amino groups. Erythrocyte membrane oligosaccharides have been oxidized by periodate or by galactose oxidase, and the resulting aldehydes labeled with biotin hydrazide.
The avidin-biotin complex in electron microscopy seems especially appropriate for seqential staining procedures, as well as for visualization of reaction sites of biotin-labeled, low-molecular-weight reagents.
Keywords: ferritin, Acholeplasma laidlawii, erythrocytes
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVIGAD G., AMARAL D., ASENSIO C., HORECKER B. L. The D-galactose oxidase of Polyporus circinatus. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2736–2743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. M., Wilchek M., Katchalski E. Irreversible inhibition of biotin transport in yeast by biotinyl-p-nitrophenyl ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2604–2607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M. Lipid bilayer structure in the membrane of Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):153–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M. AVIDIN. 1. THE USE OF (14-C)BIOTIN FOR KINETIC STUDIES AND FOR ASSAY. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj0890585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Hakomori S. I. External labeling of cell surface galactose and galactosamine in glycolipid and glycoprotein of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4311–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam J. M., Morowitz H. J. Characterization of the plasma membrane of Mycoplasma laidlawii. IX. Isolation and characterization of the membrane polyhexosamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Valentine R. C., Wrigley N. G., Ahmad F., Jacobson B., Wood H. G. Transcarboxylase. XI. Electron microscopy and subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6284–6298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraehenbuhl J. P., Jamieson J. D. Solid-phase conjugation of ferritin to Fab-fragments of immunoglobulin G for use in antigen localization on thin sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1771–1775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao T. H., Gallop P. M., Blumenfeld O. O. Modification of sialyl residues of sialoglycoprotein(s) of the human erythrocyte surface. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8247–8253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Singer S. J. Ferritin-conjugated plant agglutinins as specific saccharide stains for electron microscopy: application to saccharides bound to cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):942–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Topography of membrane concanavalin A sites modified by proteolysis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 18;239(94):193–197. doi: 10.1038/newbio239193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHICK A. F., SINGER S. J. On the formation of covalent linkages between two protein molecules. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2477–2485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N., Smith P. F., Koostra W. L. The lipid composition of Mycoplasma laidlawii strain B. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(3):329–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1070329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Dawson G. Topographical distribution of complex carbohydrates in the erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2135–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten L., Ashwell G. Studies on the chemical and enzymatic modification of glycoproteins. A general method for the tritiation of sialic acid-containing glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1889–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N. A technique for mapping transfer RNA genes by electron microscopy of hybrids of ferritin-labeled transfer RNA and DNA: the phi-80hpsu+3-system. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;78(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]