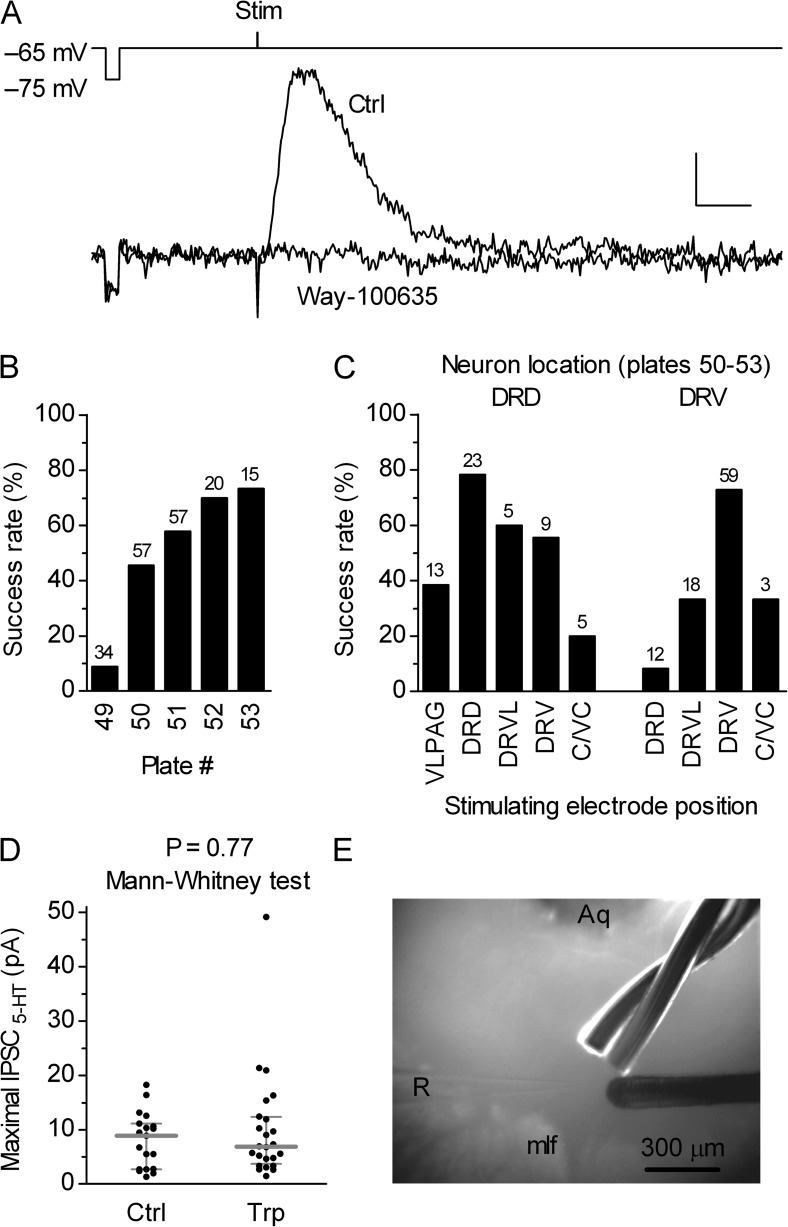
Figure 1.
Relatively inconspicuous evoked IPSC5-HT in the DRN serotonergic neurons. (A) Electrical stimulation–evoked serotonergic postsynaptic current in a serotonergic cell is inhibited by the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist Way-100635 (50 nM). Superimposed traces are averages of 11 and 7 individual traces recorded 0–5 min before (Ctrl) and after 7–10 min of Way-100635 application. Bars, 0.5 s, 6 pA. The recording electrode voltage command and the timing of the stimulus are shown above the traces. The voltage step (10 mV) preceding the stimulus was used to monitor the input resistance (RIN). The stimulus artifact is truncated. (B) Histogram summarizing percent of successfully evoked IPSC5-HT in the DRN serotonergic neurons with respect to the slice rostrocaudal level. Numbers of attempts are indicated above the bars. Plate numbers correspond to those of the rat brain atlas (Paxinos and Watson, 1998). (C) Histogram showing percent of successfully evoked IPSC5-HT in the centrocaudal part of the DRN compared with the recorded neuron location and stimulation electrode position. Numbers of attempts are indicated above the bars. DRD, dorsal raphe dorsal subnucleus; DRV, dorsal raphe ventral subnucleus; VLPAG, ventrolateral periaqueductal gray; DRVL, dorsal raphe ventrolateral subnucleus; C/VC, caudal/ventrocaudal in longitudinal slice preparation. (D) Scatter plot of the maximal IPSC5-HT amplitudes in a subset of experiments in which IPSC5-HT were evoked by using the most effective arrangement, i.e., with both the recording neuron and the stimulating electrode located in the dorsal raphe ventral subnucleus (shown in E). Comparison of responses obtained in control conditions (Ctrl; mean of 8.0 pA; median of 8.9 pA; n = 19; normal distribution; P = 0.57; D’Agostino and Pearson omnibus test) and in the presence of 5-HT precursor Trp (10 µM; mean of 10.0 pA; median of 6.9 pA; n = 24; nonnormal distribution; P < 0.0001; D’Agostino and Pearson omnibus test) revealed no significant differences between groups, indicating that the observed, relatively small maximal amplitude IPSC5-HT in the DRN are not caused by the reduced level of 5-HT in brain slice preparation. Symbols represent single experiments. Bars represent median with interquartile range. (E) Photograph illustrating the most effective electrode placement for evoking IPSC5-HT in the DRN serotonergic neurons. In 300-µm-thick slices containing the centrocaudal part of the DRN (corresponding to plates 51–53), this arrangement resulted in an ∼90% success rate and the highest amplitudes of successfully evoked responses (shown in D). Two stimulating electrodes, one twisted and one concentric (right side), are positioned in the dorsal raphe ventral subnucleus ∼200 µm distant form the recording electrode (R). Aq, aqueduct; mlf, medial longitudinal fasciculus.