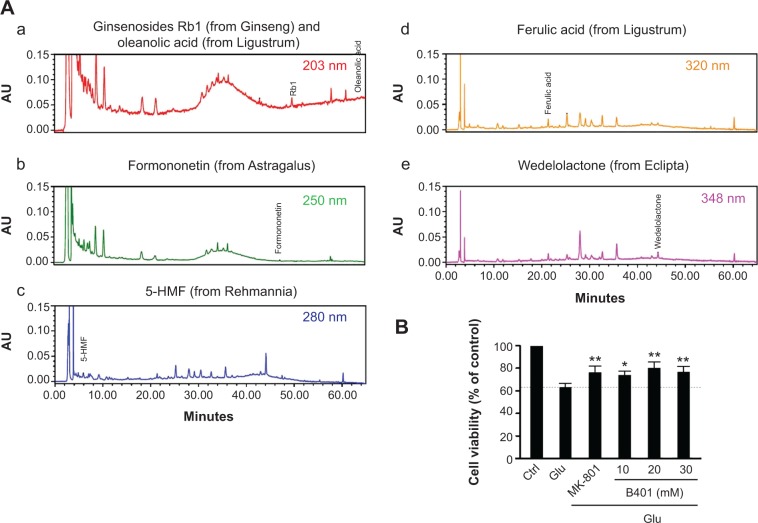
Figure 1.
Chromatographic fingerprint analysis and cell viability assay for the Chinese herbal formula B401.
Notes: (A) HPLC fingerprint of the herbal formula B401. Characteristic peaks of B401, ie, (a) ginsenosides Rb1 (molecular formula: C54H92O23; molecular weight: 1,109.3 g/mol; from Panax ginseng) and oleanolic acid (molecular formula: C30H48O3; molecular weight: 456.7 g/mol; from Ligustri fructus), (b) formononetin (molecular formula: C16H12O4; molecular weight: 268.3 g/mol; from Astragalus membranaceus), (c) 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (molecular formula: C6H6O3; molecular weight: 126.1 g/mol; from Rehmannia glutinosa), (d) ferulic acid (molecular formula: C10H10O4; molecular weight: 194.2 g/mol; from L. fructus), (e) wedelolactone (molecular formula: C16H10O7; molecular weight: 314.3 g/mol; from Eclipta prostrata), were identified and marked at the corresponding peaks in the fingerprint. (B) Cell viabilities of RA-induced SH-SY5Y cells with glutamate treatment for 24 hours in the absence or presence of the B401 at indicated doses, or NMDA receptor antagonist, MK-801. Glutamate-treated SH-SY5Y cell viabilities were significantly increased under B401 (B401, n=6 for each B401 dose treatment) and MK-801 treatment (MK-801, n=6) individually than their control (n=6). Values are mean ± SEM (**P<0.01, *P<0.05, two-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls multiple comparisons posttest).
Abbreviations: AU, arbitrary perfusion units; 5-HMF, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural; Ctrl, control; Glu, glutamate; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; RA, retinoic acid; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate; SEM, standard error of the mean; ANOVA, analysis of variance.