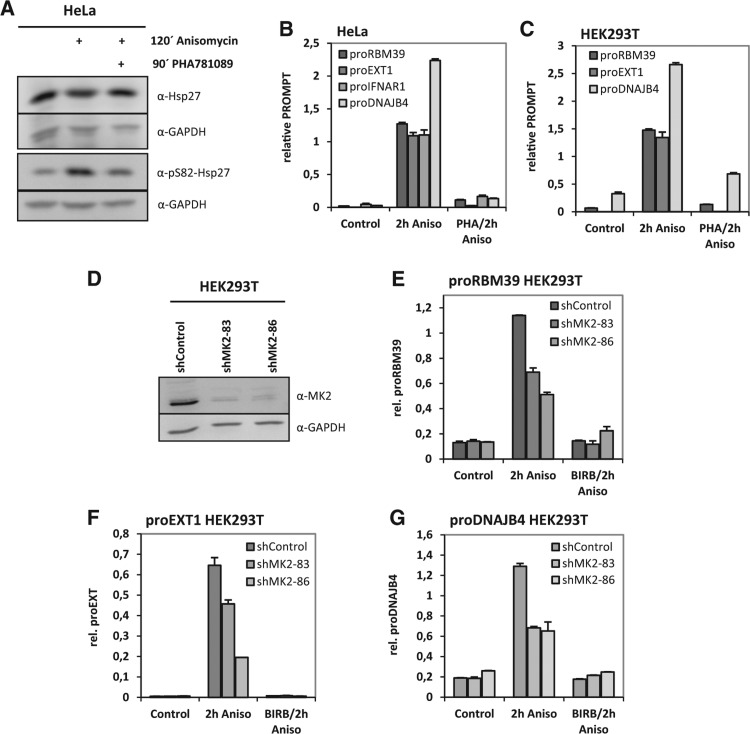
FIGURE 5.
PROMPTs accumulation is sensitive to inhibition of the p38MAPK-activted kinase MK2 in HeLa and HEK293T cells. (A) Prior to 2 h anisomycin-stimulation HeLa cells were preincubated for 90 min with MK2-inhibitor PHA781089 (15 µM). The phosphorylation of MK2's bona fide substrate Hsp27 was monitored through Western blot for pS82-Hsp27. Blots for total Hsp27 and GAPDH served as loading controls. (B) Under the same conditions as in A. PROMPTs RNA levels were determined and are shown as x-fold inductions. MK2-inhibition led to a strong down-regulation of PROMPTs levels under these conditions. (C) PROMPTs were detected in HEK293T cells. Although up-regulation of proIFNAR1 was not detectable in these cells, the anisomycin-induction of proRM39 and proEXT1 was highly sensitive to the p38MAPK-activated kinase MK2 as shown by qRT-PCR. (D) Three different stable HEK293T cell lines expressing two distinct MK2-specific shRNAs and a sh-control-RNA were generated. MK2-knockdown efficacy was controlled through blotting for MK2. GAPDH served as a loading control. MK2 levels were strongly reduced in the two MK2-specific knockdown cell lines when compared with the control cell line. (E–G) The anisomycin-induced levels of proRBM39 (E), proEXT1 (F), and proDNAJB4 (G) were assayed in the control and knockdown cell lines. Both knockdown cell lines showed reduced PROMPTs levels upon anisomycin stimulation compared with the control cell line. Notably, PROMPTs levels were further reduced by pretreatment of the cells with the p38-inhibitor BIRB796. All graphs are displayed with standard deviations. All experiments were performed independently a minimum of two times and showed similar effects.