Fig. 1.
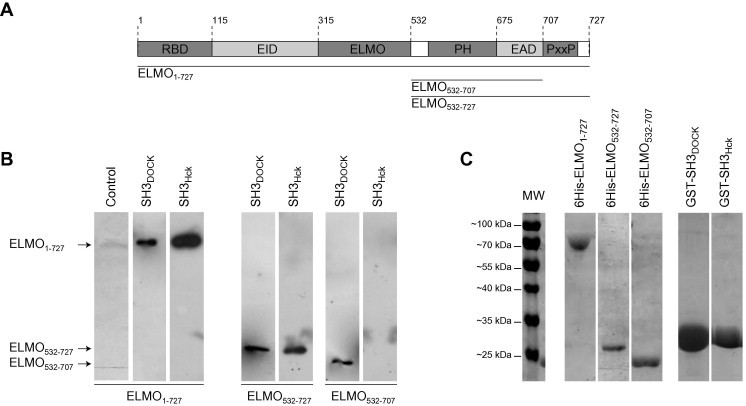
Binding of ELMO1 domains on immobilized SH3 domains of Hck and DOCK180. (A) Schematic representation of the different domains of ELMO1: The wild type ELMO1 protein (ELMO1–727), the C-terminal domain with (ELMO532–727) or without the polyproline motif (ELMO532–707) used in this study are indicated. RBD: Rho-Binding Domain; EID: ELMO Inhibitory Domain; ELMO: ELMO conserved region; PH: Pleckstrin Homology domain; EAD: ELMO Autoregulatory Domain; PxP: Polyproline motif. (B) SH3Hck binding to ELMO1 is in vitro dependent of ELMO1 polyproline motif, SH3DOCK is not: Recombinant 6His-tagged wild type ELMO1, its various deletion mutants and GST-tagged SH3 domains of Hck and DOCK180 were bacterially produced and purified from BL21 (DE3) E. coli. ELMO1 domains were incubated with immobilized either GST-fused SH3DOCK or SH3Hck and after elution, ELMO1 constructs were detected by anti-6His immuno-western blotting. (C) Coomassie-blue stained gel of the purified protein constructs overexpressed in E. Coli: Purity of ELMO and SH3 domains constructs was analyzed after FPLC purification by Coomassie-blue stained polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in denaturing conditions (12% slab gels). Each construct migrates at its expected apparent molecular weight.
