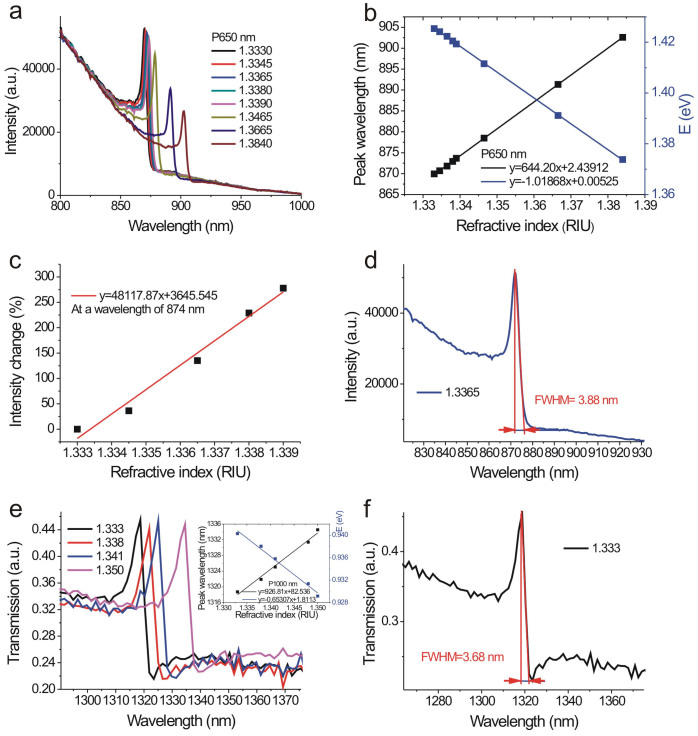
Figure 4. Refractive index sensing capabilities of the capped gold nanoslits made by the template stripping method.
(a) The intensity spectra of the capped gold nanoslits with a 650-nm period in various water/glycerin mixtures for a normally-incident TM-polarized wave. (b) The resonant peak wavelength and energy against the refractive index of the outside medium. The slopes of the fitting curves show that the refractive index sensitivities were 644 nm/RIU and 1.018 eV/RIU. (c) The normalized intensity change against the refractive index of the outside medium. The slope of the fitting curve shows that the intensity sensitivity was 48,117%/RIU. (d) The measured fwhm bandwidth of the Fano resonant peak in glycerin/water mixture (n = 1.3365) was 3.88 (fwhm = 0.0063 eV). The extremely sharp resonance leads to a high-quality factor up to 224. (e) The transmission spectrum of the capped nanoslits with a period of 1,000 nm in various water/glycerin mixtures for normally-incident TM-polarized light. The inset shows the refractive index sensitivities were 926 nm/RIU and 0.653 eV/RIU. (f) The enlarged transmission spectrum of the capped nanoslits with a period of 1,000 nm in water. The measured fwhm bandwidth of the Fano resonant peak was 3.68 nm (0.0026 eV).