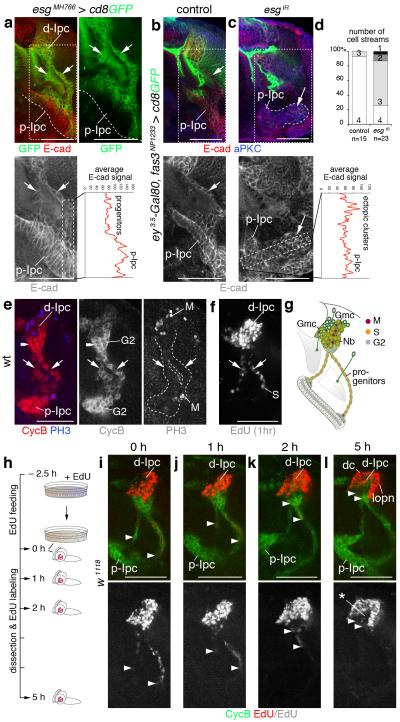
Figure 3. Migratory progenitors arise by epithelial-mesenchymal transition and require escargot (esg).
(a) Progenitors, leaving the p-Ipc (line) and entering cell streams (arrows), upregulate esgMH766-Gal4, UAS-cd8GFP (green) and downregulate E-cadherin (E-cad, red). (b,c) Compared to controls (b), Ipc-specific knockdown of esg (esgIR) using fasciclin3 (fas3)NP1233-Gal4 induces ectopic clusters continuous with the p-Ipc (large arrows, c) that maintain strong E-cad expression. Small arrows indicate one of the streams (b). Graphs show average E-cad fluorescence signals in boxes in left-hand higher-magnification panels. (d) Quantification of main cell stream numbers in controls and upon esg knockdown. (e) p-Ipc neuroepithelial cells strongly express CyclinB (CycB, red). After leaving the p-Ipc, progenitors express phosphoHistone 3 (PH3, blue). (f) Progenitors in streams (arrows), labeled by 1 hour EdU incubation, are in S phase. They enter G2 phase at the d-Ipc base (double arrowheads, e). d-Ipc neuroblasts and ganglion mother cells (Nb/Gmc) undergo S phase and mitosis (e,f). (g) Summary of Ipc cell cycle profile. (h–l) In EdU pulse-chase experiments, brains of wandering third instar larvae were assessed at 0, 1, 2 and 5 hours after 2.5 hours EdU feeding. Arrowheads indicate the most proximal EdU+ (red) progenitors within streams. The distance of EdU+ progenitors to the p-Ipc gradually increases, consistent with migration. After 5 hours, d-Ipc neuroblasts/Gmcs above CycB (green) expressing progenitors are no longer labeled with EdU (asterisk, l). Labeling persists in distal cells (dc) and lobula plate neurons (lopn). For genotypes and sample numbers, see Supplementary Table 1. Scale bars, 50 μm.