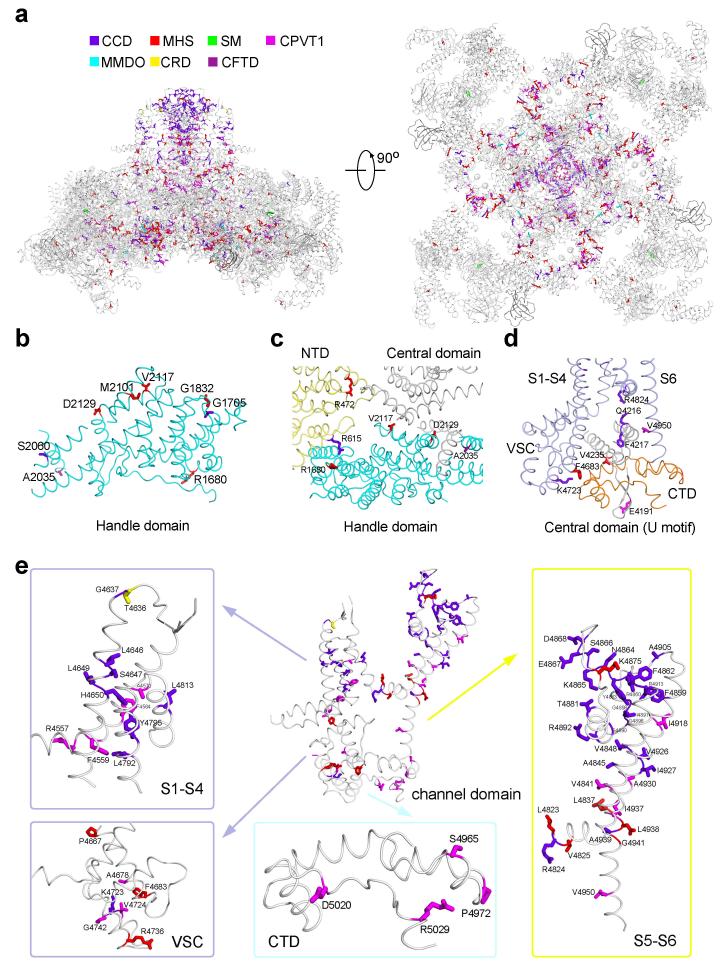
Extended Data Figure 9. Mapping of the disease-associated point mutations onto the structure of the RyR1 channel domain.
a, The residues that are targeted for disease-derived mutations are highlighted by different colors: purple blue for CCD (central core disease), red for MHS (malignant hyperthermia susceptibility), green for SM (samaritan myopathy), cyan for MMDO (minicore myopathy with ophthalmoplegia), yellow for CRD (core/rod disease), dark purple for CFTD (congenital fiber type disproportion), and magenta for CPVT1 (catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia type 1). Please refer to the Supplementary Table 1 for details of these mutations. b, Disease-related mutations in the Handle domain. The concerned residues, which are positioned on the surface of the Handle domain, may be involved in the interaction with modulators or other domains within RyR1. c, Disease-related residues aligning the inter-domain interface between NTD, the Handle and Central domains. d, Representative disease-related residues involved in the interaction between the Central domain and the channel domain. e, The channel domain represents a hotspot for mutations associated with a number of diseases. Please refer to Extended Data Fig. 7 and Supplementary Table 1 for details of the mutations.