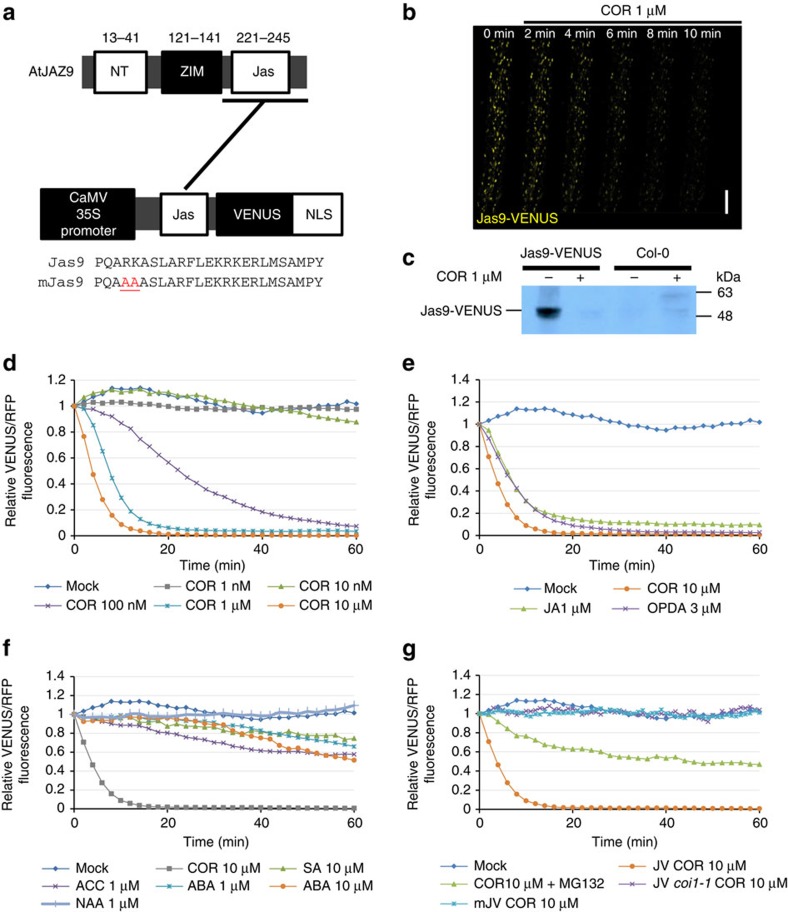
Figure 1. Jas9-VENUS is a biosensor for bioactive JA perception.
(a) Schematic representation of the AtJAZ9 gene, the Jas9-VENUS and mJas9-VENUS constructs, as well as the protein sequences of their respective Jas motif (Jas, Jas motif; NLS, nuclear localization signal; NT, amino terminus; ZIM, ZIM motif). Numbers above the schematic represent amino acid position. (b) Time-course confocal laser scanning micrographs of Jas9-VENUS at the indicated time points after treatments with 1 μM coronatine (COR; scale bar, 100 μm). (c) Western blot analysis of total protein extracts of Jas9-VENUS and Col-0 seedlings treated for 30 min with or without 1 μM COR and probed with an anti-GFP antibody (uncropped western blotting is shown in Supplementary Fig. 1d). (d) Time-course quantification of Jas9-VENUS fluorescence, normalized to H2B-RFP fluorescence, in response to various concentrations of coronatine (n=3). (e) Time-course quantification of Jas9-VENUS fluorescence, normalized to H2B-RFP fluorescence, in response to JA-Ile precursors JA and OPDA (n=2). (f) Time-course quantification of Jas9-VENUS fluorescence, normalized to H2B-RFP fluorescence, in response to auxin (α-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA)), ABA, ACC (ethylene precursor) or SA (n=2). (g) Time-course quantification of Jas9-VENUS fluorescence, normalized to H2B-RFP fluorescence, in response to treatments with COR in a WT or a coi1-1 mutant, in response to COR and MG132 (proteasome inhibitor) treatments, and of mJas9-VENUS fluorescence, normalized to H2B-RFP fluorescence, in response to COR (n=2). All the data shown derive from a representative experiment and the number of replications of each experiment is indicated. JV, Jas9-VENUS; mJV, mJas9-VENUS.