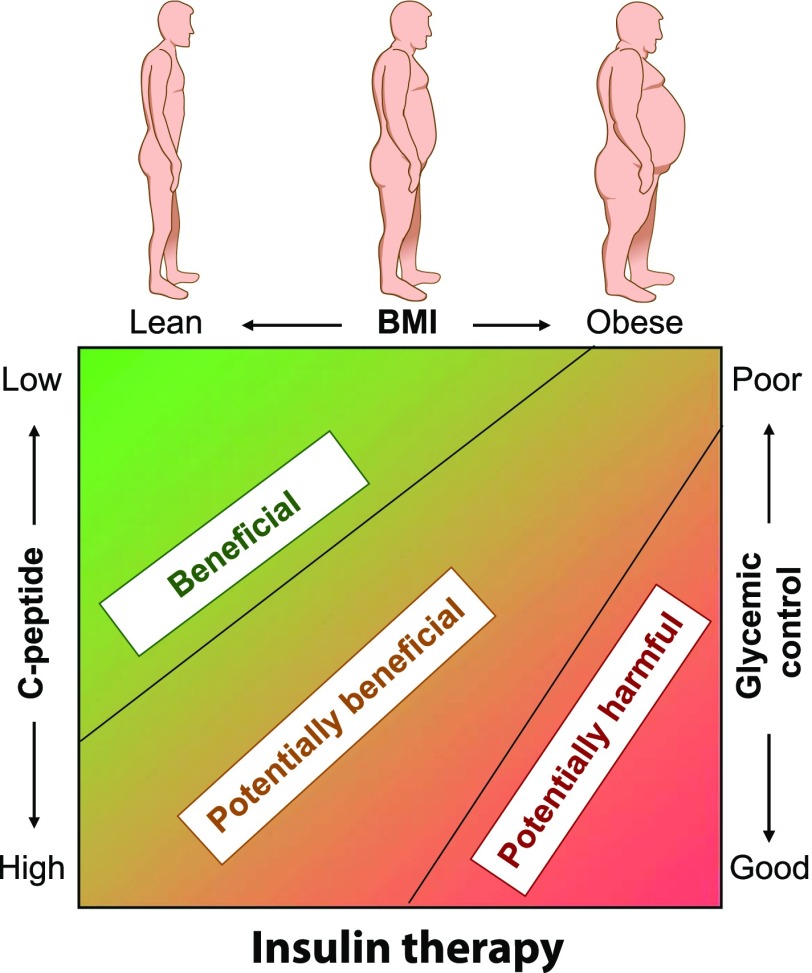
Figure 4.
The appropriateness of insulin therapy in patients with T2D. The need for insulin therapy depends on whether it is being used as replacement in insulin-deficient patients (less likely to cause harm) or to override IR (more likely to cause harm). Insulin-deficient patients are more likely to be lean and in neutral or negative energy balance, with low C-peptide levels and poor glycemic control. Insulin-induced harm is more likely to occur in overweight and obese subjects with IR and high C-peptide levels and an inability to achieve negative energy balance through lifestyle change. In these patients, lifestyle and pharmacological therapies aimed at reversing the excess nutrient imbalance are more advisable than insulin therapy.