Figure 7.
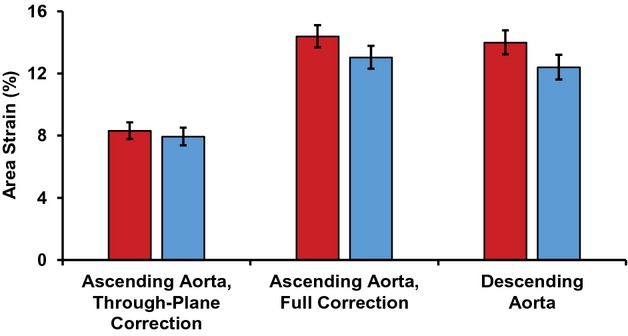
Lumen area strain of the ascending and descending aorta for women (red) and men (blue). Through‐plane correction refers to circumferential ascending aortic strain that has been corrected for through‐plane motion only; full correction refers to circumferential ascending aortic strain that has been corrected for through‐plane motion and longitudinal strain; and descending aorta refers to circumferential strain in the descending aorta. Through‐plane corrected strain was significantly smaller than longitudinally corrected strain (P<0.001), with no sex difference (P=0.058), although there was a sex interaction (P=0.019) because of a greater longitudinal strain correction in women. Through‐plane corrected strain was also markedly less than descending aortic strain (P<0.001), with a significant sex difference (P=0.012), but no sex interaction (P=0.10). In contrast, longitudinally corrected strain was comparable to descending aortic strain (P=0.12), with a strong sex difference (P=0.001) and no sex interaction (P=0.7). Strains were square root transformed for statistical analyses and results were squared for presentation. Error bars represent 95% CI.
