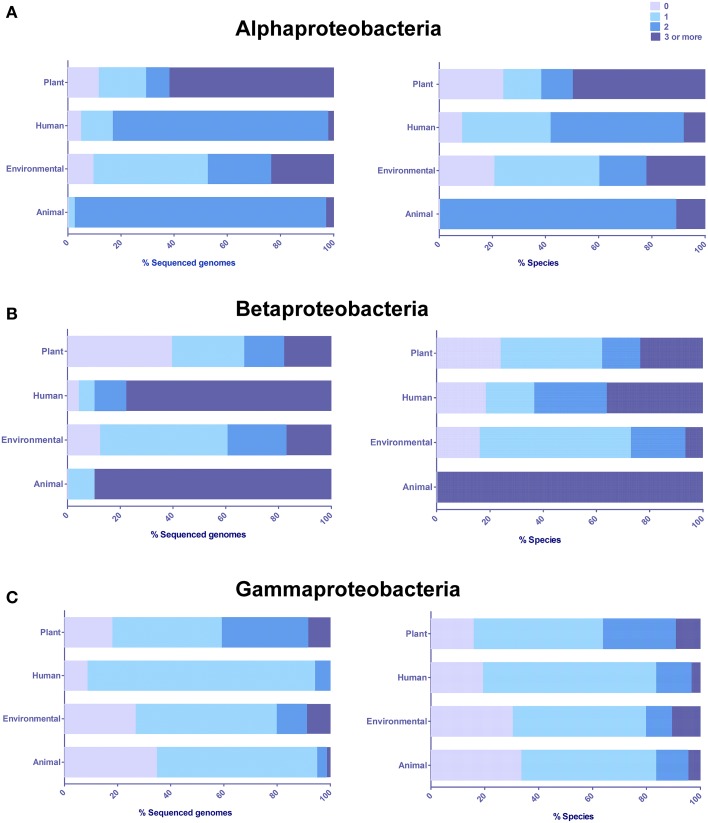
Figure 2.
Distribution and abundance of LuxR solos in different classes based on the origin or predominant niche specificity of bacterial species harboring these proteins. (A) Alphaproteobacteria (B) Betaproteobacteria, (C) Gammaproteobacteria. Plant, Plant-associated bacteria; Human, Human-associated bacteria; Environmental, Environmental isolates; and Animal, Animal-associated bacteria. Some bacterial species were placed in more than one category. The presence of LuxR solos was inferred by analyzing QS domain LuxR proteins of Interpro database, IPR005143, and correlated to niche specificity by generating contingency tables in Microsoft Excel.