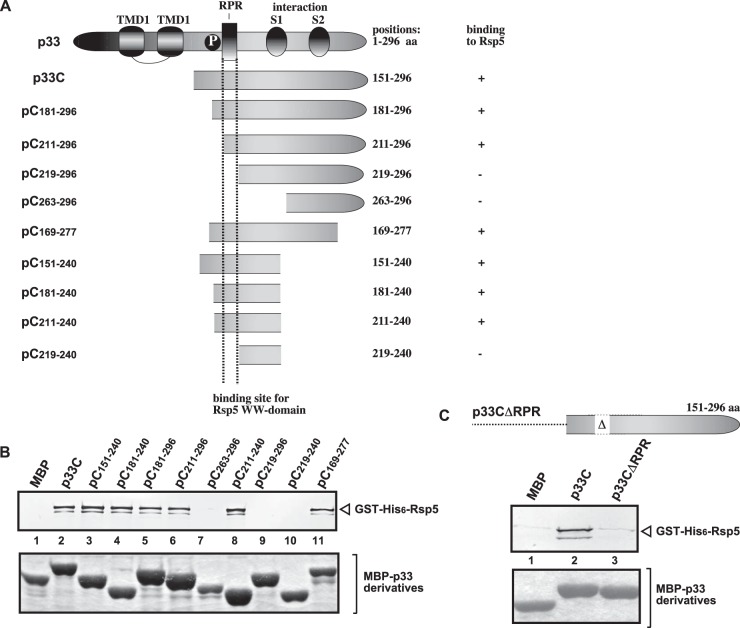
FIG 1.
Defining the sequence within the TBSV p33 protein needed for binding to the Rsp5p WW-domain protein in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of the TBSV p33 and its truncated derivatives used in the affinity-binding assay. The various domains include the following: TMD, transmembrane domain; RPR, arginine-proline-rich RNA-binding domain; P; phosphorylated serine and threonine; S1 and S2 subdomains involved in p33–p33/p92 interaction. (B) Affinity binding (pulldown) assay to detect interaction between GST-His6-tagged Rsp5p and the MBP-tagged viral p33 protein derivatives. The MBP-tagged viral proteins produced in E. coli were immobilized on amylose-affinity columns. Then, GST-His6-Rsp5p expressed in E. coli was passed through the amylose-affinity columns with immobilized MBP-tagged proteins. The affinity-bound proteins were eluted with maltose from the columns. (Top) The eluted proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-His antibody to detect the amount of GST-His6-Rsp5p specifically bound to MBP-tagged viral proteins. (Bottom) SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified MBP-p33 and its derivatives. (C) Pulldown assay to detect interaction between GST-His6-tagged Rsp5p and the MBP-tagged p33CΔRPR protein. See further details in panel B.