FIG 5.
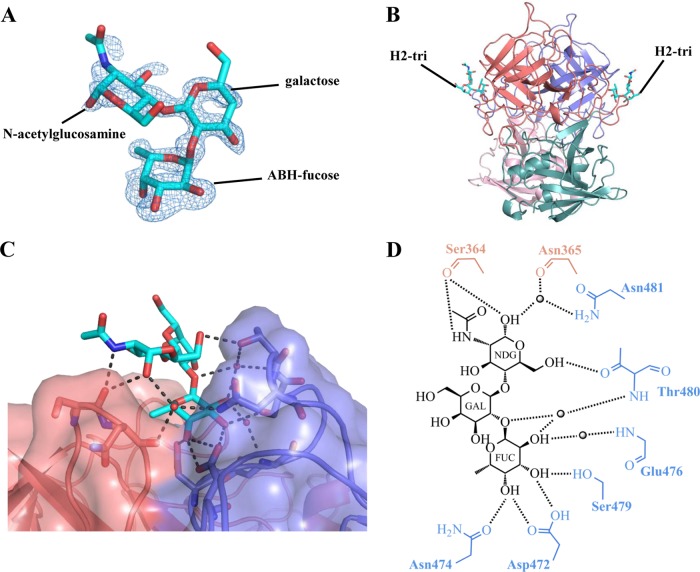
RHDVb P domain and H2-tri interactions. H2-tri is an α-l-fucose-(1-2)-β-d-galactose-(1-4)-N-acetyl-β-d-glucosamine. The reducing-end hydroxyl group was fixed in α position in H2-tri (underlined). (A) The Fo-Fc simulated annealing difference omit map (blue) was contoured at 3.0 σ. The electron density for H2-tri (cyan sticks) was clearly visible for ABH-fucose and less defined for galactose and N-acetylglucosamine. (B) H2-tri bound to the dimeric interface on the side of the P dimer. (C) Closeup surface-and-ribbon representation of the RHDVb P dimer showing the bound H2-tri. (D) The H2-tri binding interaction with RHDVb P dimer, where the black dotted lines represent the hydrogen bonds and the sphere represents water molecules (fucose, FUC; galactose, GAL; N-acetylglucosamine, NDG). For simplicity, only the backbone is shown for residues that were backbone mediated. Hydrogen bond distances were less than 3.2 Å, although the majority were ∼2.8 Å.