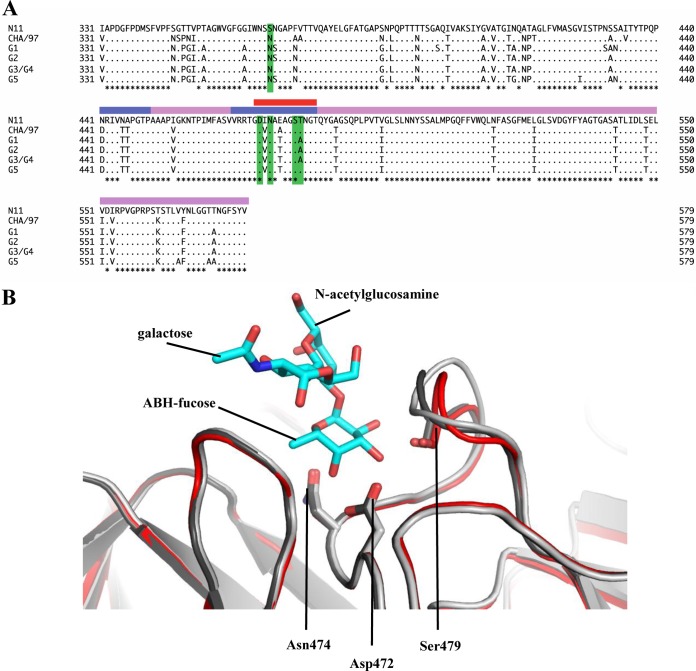
FIG 6.
Amino acid sequence alignment of the partial RHDV P domains and structural analysis of the loop that binds the ABH-fucose. (A) The P domains of different RHDV strains, N11 (JX133161; RHDVb), CHA/97 G6 (DQ205345; RHDVa), G1 (Z49271), G2 (AF402614), G3/G4 (FR823354), and G5 (AM085133), were aligned using Clustal X (partial sequences are shown). The P domain was divided into P1 (pink) and P2 (slate) subdomains as previously described (12). The residues having a direct hydrogen bond with HBGAs were highlighted (green). The flexible loop region was between residues 472 and 483 (red bar). The asterisks represent conserved amino acids residues. (B) Superposition and closeup view of the flexible loop (residues 472 to 483) of two unbound RHDVb dimers (light and dark gray) and one RHDVb H2-tri dimer (red), showing bound H2-tri (cyan sticks). The flexible loop, shown in various conformations, contained three residues (side chains of Asp472, Asn474, and Ser479) that were involved in binding of the ABH-fucose of H2-tri. The side chain of Ser479, which interacted with N-acetylglucosamine, was not modeled into the loop of one unbound RHDVb dimer due to poor electron density. However, on the corresponding loop of the second monomer, the electron density of the Ser479 side chain was clearly defined (data not shown).