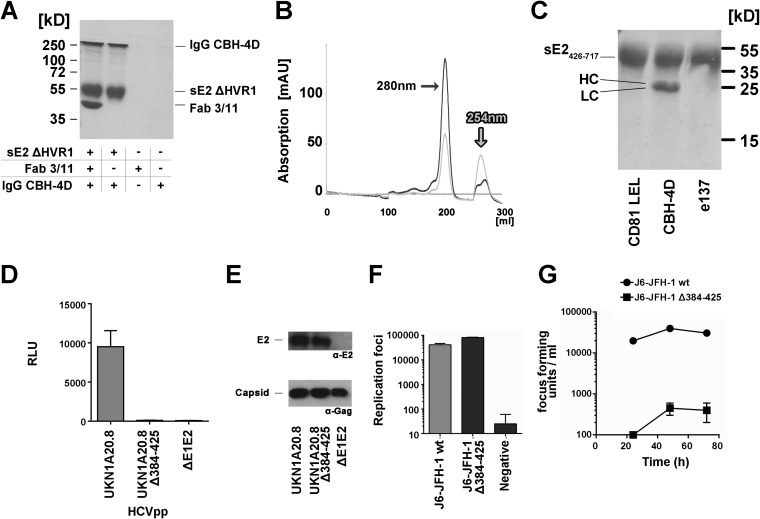
FIG 6.
Effect of deletion of aa 412 to 425 on protein folding and infectivity. (A) Pulldown assay of the conformation-dependent nonneutralizing human antibody CBH-4D (43) by sE2 ΔHVR1 and the Fab 3/11-sE2 ΔHVR1 complex indicating that Fab 3/11 binding does not affect the overall glycoprotein fold. (B) Elution profile of sE2426–717 (UKN2B2.8) from a Superdex200 size exclusion column. AU, absorption units. (C) Pulldown assay of CD81-LEL, Fab CBH-4D, and Fab e137 by sE2426–717 reveals an intact overall glycoprotein fold but severely impaired binding to the CD81 binding site. (D to G) Infectivity of deletion mutants in HCVcc and HCVpp models of infection. (D) The E1/E2 genes of the highly infectious primary isolate UKN1A20.8 were used as the template for the deletion of amino acids 384 to 425. HCVpp possessing wt and mutant glycoproteins were used to infect Huh7 cells. Infectivity measurements were performed with a luciferase reporter gene. Only target cells inoculated with wild-type HCVpp exhibited luciferase activity. RLU, relative light units. (E, top) Western blot analysis of HCVpp using the linear anti-E2 MAb ALP98 reveals similar E2 incorporation levels for wt and mutant HCVpp (lanes 1 and 2, respectively). (Bottom) The amount of particles was verified by Western blotting using an anti-Gag antibody. (F and G) A plasmid encoding a chimeric J6/JFH-1 virus was used as the template for the deletion of amino acids 384 to 425. RNA transcripts of wt and mutant viruses were electroporated into Huh7.5 cells. Results are presented as means and standard deviations from duplicate experiments. (F) RNA replication was assessed by intracellular staining for the presence of HCV NS5a in electroporated cells. Both constructs replicated similarly, with the deletion mutant having slightly enhanced replication. (G) Cell supernatants harvested 24, 48, and 72 h after transfection were assessed for the presence of infectious virus by infecting naive Huh7.5 cells. Infectious wild-type virus was produced, while no infectivity was observed for the mutant virus.