Abstract
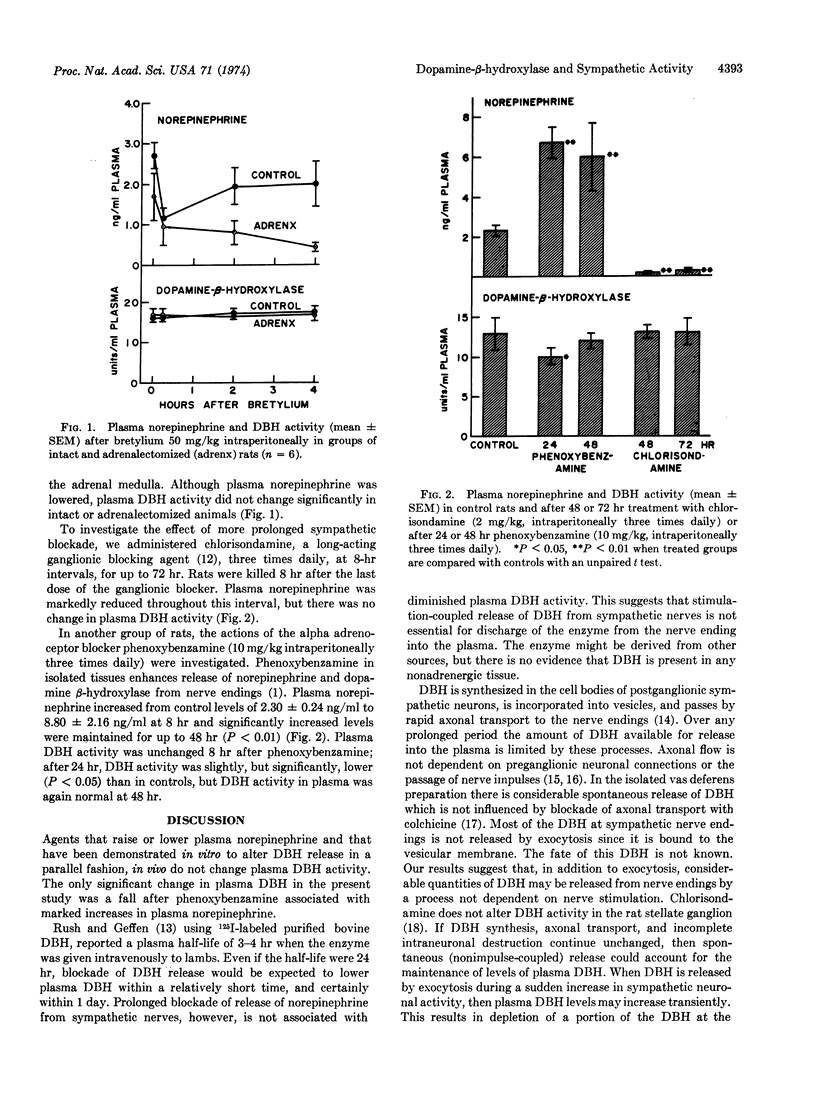
Plasma norepinephrine and dopamine β-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.17.1) activity were measured in rats. Adrenergic neuron blockade with bretylium for 4 hr and ganglion blockade with chlorisondamine for 72 hr lowered plasma norepinephrine. Neither treatment altered plasma dopamine β-hydroxylase activity. Phenoxybenzamine for up to 48 hr markedly raised plasma norepinephrine and transiently lowered plasma dopamine β-hydroxylase at 24 hr. Prolonged pharmacological modification of sympathetic nervous activity and plasma norepinephrine were not attended by parallel changes in circulating dopamine β-hydroxylase activity. Plasma dopamine β-hydroxylase activity does not appear to be a sensitive index of prolonged alterations in sympathetic neural activity. Norepinephrine in plasma, however, appears to reflect sensitively and accurately the rate of release of the neurotransmitter.
Keywords: norepinephrine, adrenergic neuronal blockade, bretylium, chlorisondamine, phenoxybenzamine
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOURA A. L., GREEN A. F. ADRENERGIC NEURONE BLOCKING AGENTS. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1965;5:183–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.05.040165.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström A. Axoplasmic transport (with particular respect to adrenergic neurons). Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Jun 17;261(839):325–358. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen L. B., Livett B. G. Synaptic vesicles in sympathetic neurons. Physiol Rev. 1971 Jan;51(1):98–157. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen L. B., Rush R. A. Transport of noradrenaline in sympathetic nerves and the effect of nerve impulses on its contribution to transmitter stores. J Neurochem. 1968 Sep;15(9):925–930. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb11634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D., Alexander R. W., Lovenberg W., Keiser H. R. Human serum dopamine- -hydroxylase. Relationship to hypertension and sympathetic activity. Circ Res. 1973 May;32(5):594–599. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.5.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Jarrott B. Modification of an enzyme radiochemical assay procedure for noradrenaline. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 May;19(5):1841–1843. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXWELL R. A., PLUMMER A. J., ROSS S. D., DANIEL A. I., SCHNEIDER F. Factors affecting the blood pressure response of mammals to the ganglionic blocking agent, chlorisondamine chloride. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Jul;123(3):238–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Brimijoin S., Axelrod J. Induction of dopamine- -hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase in rat hearts and sympathetic ganglia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Jul;182(1):116–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Weinshilboum R., Axelrod J. A sensitive enzymatic assay for dopamine- -hydroxylase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Sep;178(3):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush R. A., Geffen L. B. Radioimmunoassay and clearance of circulating dopamine- -hydroxylase. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(3):444–452. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.3.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saelens J. K., Schoen M. S., Kovacsics G. B. An enzyme assay for norepinephrine in brain tissue. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Jun;16(6):1043–1049. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanberg S. M., Stone R. A., Kirshner N., Gunnells J. C., Robinson R. R. Plasma dopamine beta-hydroxylase: a possible aid in the study and evaluation of hypertension. Science. 1974 Feb 8;183(4124):523–525. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4124.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoa N. B., Wooten G. F., Axelrod J., Kopin I. J. Inhibition of release of dopamine- -hydroxylase and norepinephrine from sympathetic nerves by colchicine, vinblastine, or cytochalasin-B (hypogastric nerve stimulation-exocytosis-microtubules-microfilaments-guinea pig). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):520–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshilboum R. M., Kvetnansky R., Axelrod J., Kopin I. J. Elevation of serum dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity with forced immobilization. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 28;230(17):287–288. doi: 10.1038/newbio230287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshilboum R. M., Thoa N. B., Johnson D. G., Kopin I. J., Axelrod J. Proportional release of norepinephrine and dopamine- -hydroxylase from sympathetic nerves. Science. 1971 Dec 24;174(4016):1349–1351. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshilboum R., Axelrod J. Serum dopamine- -hydroxylase: decrease after chemical sympathectomy. Science. 1971 Sep 3;173(4000):931–934. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4000.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshilboum R., Axelrod J. Serum dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity. Circ Res. 1971 Mar;28(3):307–315. doi: 10.1161/01.res.28.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooten G. F., Cardon P. V. Plasma dopamine- -hydroxylase activity. Elevation in man during cold pressor test and exercise. Arch Neurol. 1973 Feb;28(2):103–106. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490200051006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


