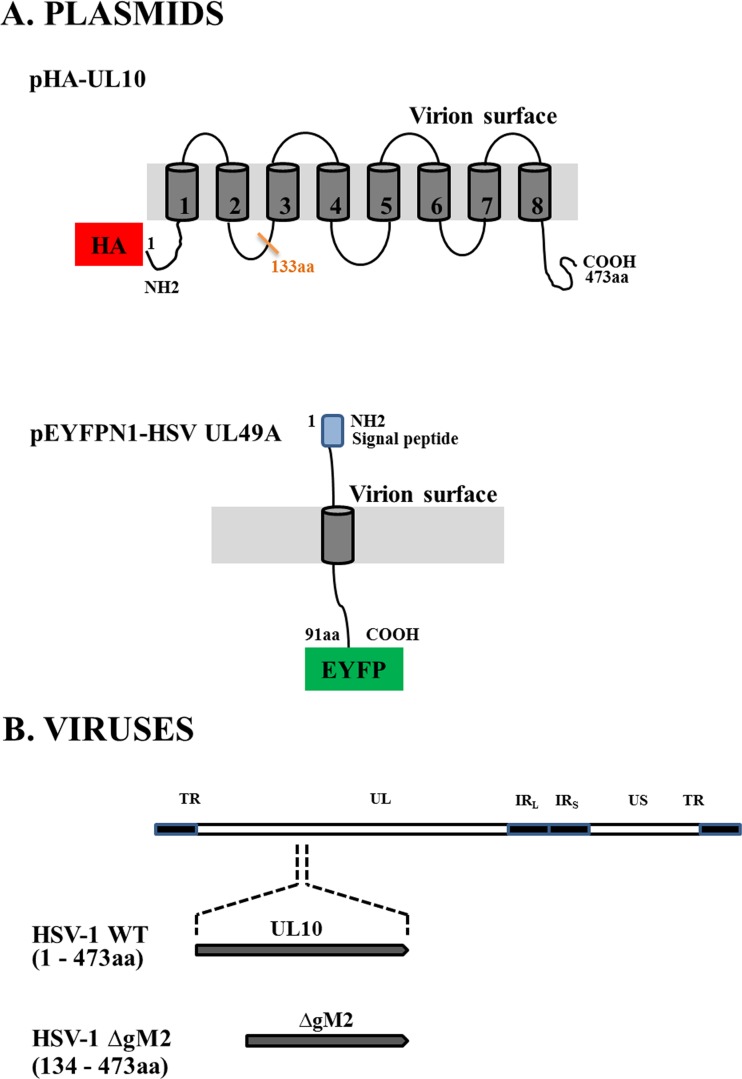
FIG 1.
Schematic view of plasmids and viruses used in this study. (A) Plasmid vectors expressing either the amino-terminal HA-tagged gM (pHA-UL10) or the carboxyl-terminal YFP-tagged gN (pEYFPN1-HSV UL49A) fusion proteins are shown. The gray areas indicate the predicted transmembrane domains. (B) The genomic map of the HSV-1 genome is showing the unique long (UL) and unique short (US) regions flanked by terminal (TR) and internal inverted (IRL and IRS) repeat sequences. In most experiments, wild-type virus coding for the full-length gM was used (473 amino acids; HSV-1 WT). Where indicated, a mutant virus coding for a truncated gM, in which the first 133 amino acids of gM were deleted (HSV-1 ΔgM2 mutant), was used.