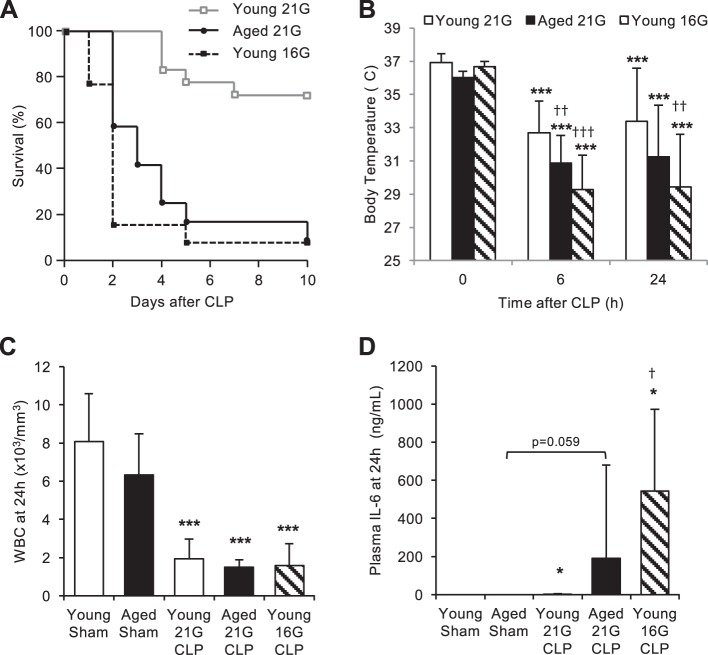
Fig. 1.
Severity of sepsis in young and aged mice after cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). A: survival study demonstrating age-dependent mortality during CLP-induced sepsis. Young and aged male C57BL/6 mice received CLP surgery with a 16-gauge (16G) or 21-gauge (21G) needle, and survival was monitored for 10 days (N = 12–18/group). There was no statistical difference between the survival curve patterns of aged mice with 21G CLP and young mice with 16G CLP (P = 0.189). No mortality was observed in age-matched sham-operated mice (data not shown). B: hypothermia of CLP-operated mice 0, 6, and 24 h after surgery. There was no statistical difference between body temperatures of aged mice with 21G CLP and young mice with 16G CLP (P = 0.102 and P = 0.380 for 6 and 24 h, respectively). C: white blood cell (WBC) count of sham- and CLP-operated mice 24 h after surgery. There was no statistical difference among the CLP groups (P = 0.68). D: circulating levels of IL-6 in sham- and CLP-operated mice 24 h after surgery. There was no statistical difference between plasma IL-6 level of aged mice with 21G CLP and young mice with 16G CLP (P = 0.27). Values are means ± SD; n = 5–8 for each group. *Statistical significance compared with sham-operated mice of the same age; †statistical significance compared with young mice with 21G CLP. One, two, or three symbols signify P < 0.05, 0.01, or 0.001, respectively.