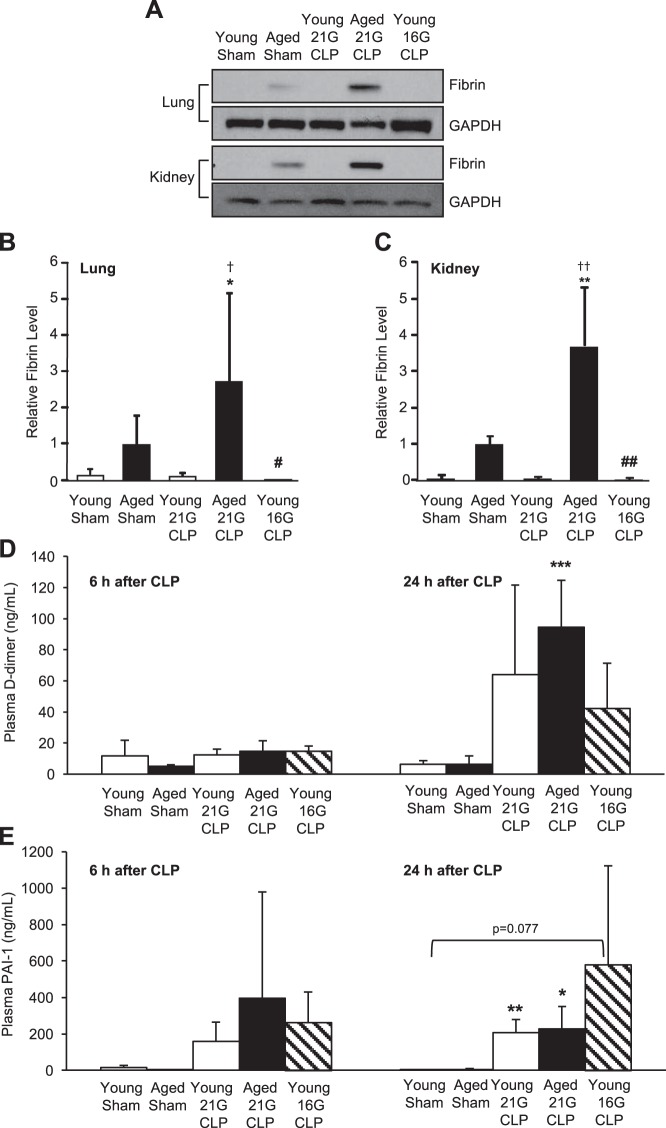
Fig. 3.
Age-dependent coagulation in the lung and kidney during sepsis. Young and aged male C57BL/6 mice received CLP surgery with a 16G or 21G needle. Age-matched sham-operated mice were used as controls. A–C: fibrin deposition in lung (B) and kidney (C) 24 h after CLP or sham surgery was assessed by Western blot analysis and quantified by densitometric analysis of individually run protein samples. Blot images shown represent pooled protein samples derived equally from 4 to 5 mice; however, individual samples were run and blotted separately for statistical analyses. Membranes were reprobed for GAPDH to assure equal protein loading, and quantified fibrin levels were adjusted for GAPDH. This analysis was performed twice in different sets of mice with the same result. Plasma levels of fibrinolytic markers d-dimer (D) and plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 (E) at 6 and 24 h after CLP or sham surgery are shown. Values are means ± SD; n = 4–8. *Statistical significance compared with sham-operated mice of the same age; †statistical significance compared with young mice with 21G CLP; #statistical significance compared with aged mice with 21G CLP. One, two, or three symbols signify P < 0.05, 0.01, or 0.001, respectively.