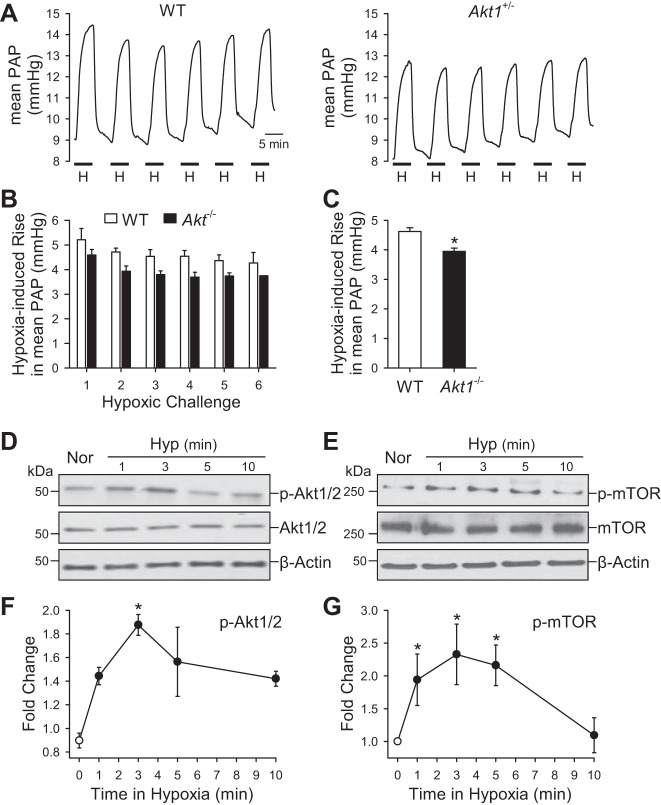
Fig. 9.
Deletion of Akt1 attenuates acute hypoxia-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction. A: representative record of PA pressure (PAP) in isolated perfused and ventilated lungs from WT and Akt−/− mice. B: summarized data (means ± SE) showing the increases in PAP induced by repeated hypoxia challenges (6 times) in isolated and ventilated lungs from WT (open bars) and Akt−/− (solid bars) mice. C: averaged data (means ± SE) showing the averaged increases in PAP induced by all hypoxic challenges in WT (n = 3) and Akt−/− (n = 3) mice. *P < 0.05 vs. WT. D–G: representative Western blot data (D and E) and time course (F and G) of hypoxia-induced increase in phosphorylation of Akt1/2 (p-Akt1/2) and mTOR (p-mTOR) in PASMC. *P < 0.05 vs. 0 min hypoxia.