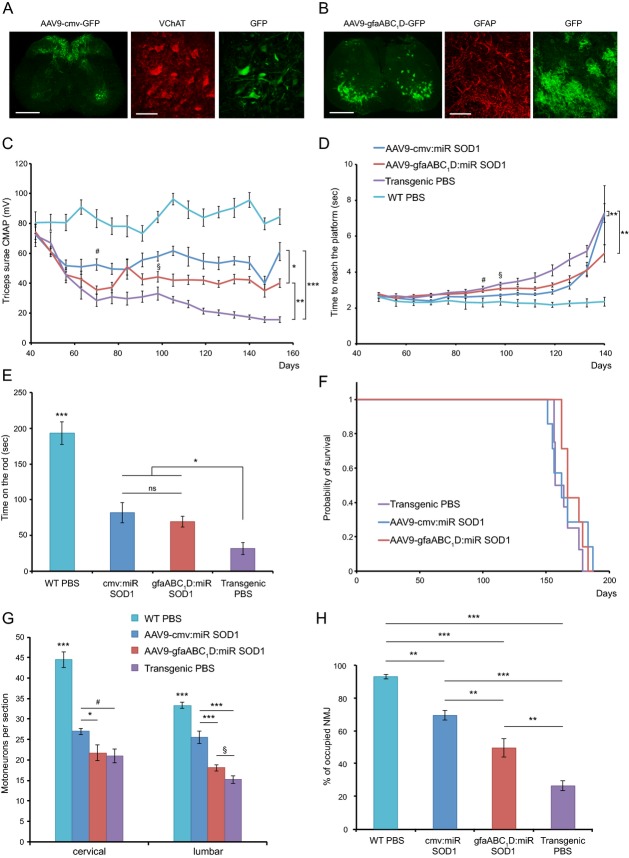
Figure 6.
Intrathecal injection of AAV-miR SOD1 to adult ALS mice shows therapeutic benefits. (A and B) Represented are lumbar sections of mice injected intrathecally with AAV9 coding for GFP. The cmv promoter leads to transgene expression preferentially in VChAT-positive motoneurons (A), whereas the gfaABC1D promoter specifically targets astrocytes (B). Scale bar: whole spinal cord, 500 μm; close-up, 80 μm. (C) CMAP values were recorded from triceps surae of treated and control animals. Neuromuscular function is partially rescued in miR: SOD1-injected animals when compared to transgenic controls. Overall, significant group effect is observed between all conditions. Note that CMAP values of the AAV9-cmv:miR SOD1 and AAV9-gfaABC1D:miR SOD1 animals start to be statistically different from values obtained for the PBS-injected G93ASOD1 mice at weeks 5 (#) and 9 (§) postinjection, respectively. (D) Evaluation of weekly swimming performances reveals overall improved motor abilities of treated animals compared to transgenic PBS mice. Significant difference in the time necessary to reach platform is observed starting at 8 weeks postinjection for the AAV9-cmv:miR SOD1 group (#) and 9 weeks postinjection for the AAV9-gfaABC1D:miR SOD1 group (§). No significant difference with the transgenic PBS mice is observed for the last time point. (E) At day 140, AAV-injected animals show significantly superior forced motor activity when using the Rotarod test as compared to transgenic PBS-injected mice. No significant difference is observed between the two miR SOD1-injected groups (F) Kaplan–Meier survival curve shows no difference in survival between treated and PBS-injected ALS mice. (G) Motoneuron counts per spinal cord section for AAV9-injected and control animals at cervical and lumbar levels. At the lumbar level motoneuron numbers are significantly increased for the AAV9-cmv:miR SOD1 group when compared to AAV9-gfaABC1D:miR SOD1 and transgenic control animals. A trend toward improved motoneuron survival is observed for the AAV9-gfaABC1D:miR SOD1 group at the lumbar level (§; P = 0.05). At the cervical level the AAV9-cmv:miR SOD1 group counts significantly more motoneurons than the AAV9-gfaABC1D:miR SOD1 group but only a trend toward improved survival (#; P = 0.06) is observed when compared to control ALS mice. (H) Neuromuscular junction integrity expressed as percentage of VAChT-positive motoneuron terminals to bungarotoxin-positive motor end plates. Innervation is partially preserved in both AAV: miR SOD1-injected groups, with significant difference being observed between the AAV9-cmv and the AAV9-gfaABC1D animals. (D–H) AAV9-cmv:miR SOD1: n = 6, AAV9-gfaABC1D:miR SOD1: n = 7, transgenic PBS: n = 8, WT PBS: n = 9. Data are expressed as mean ± standard errors of the mean deviation. One-way ANOVA and Newman–Keuls post hoc test. Two-way ANOVA and Newman–Keuls post hoc test was used for evaluation of the significance of group effect on CMAP values and swimming performance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. SOD1, superoxide dismutase 1; CMAP, compound muscular action potentials; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.