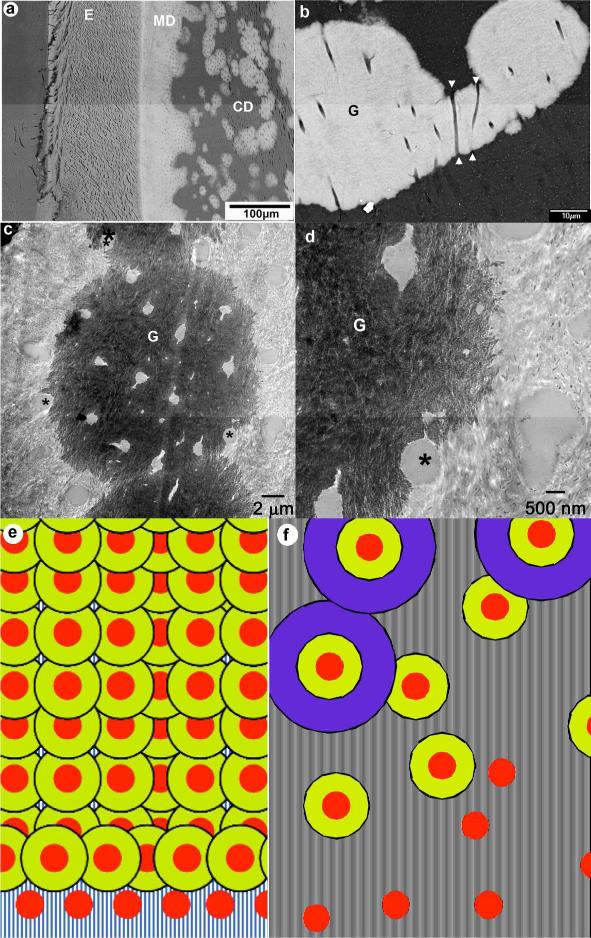
Figure 1.
a) Low magnification SEM micrograph of the DSPP KO incisor. b) Intermediate magnification SEM micrograph of circumpulpal dentin showing 3 fused mineralized globules in the nonmineralized matrix. E-enamel; CD- circumpulpal dentin; G-mineralized globules; arrowheads point toward the c) TEM micrograph of a mineralized globule. d) a close up of the micrograph in c. In c and d asterisks identify tubules at the boundary between mineralized and nonmineralized dentin matrix. e) a model of normal dentin mineralization with high nucleation density and f) dentin mineralization in DSPP KO with low nucleation density. Red circles- the nucleation sites, yellow and purple concen Figure 1. a) Low magnification SEM micrograph of the DSPP KO incisor. b) Intermediate magnification SEM micrograph of circumpulpal dentin showing 3 fused mineralized globules in the nonmineralized matrix. E-enamel; CD- circumpulpal dentin; G-mineralized globules; arrowheads point toward the c) TEM micrograph of a mineralized globule. d) a close up of the micrograph in c. In c and d asterisks identify tubules at the boundary between mineralized and nonmineralized dentin matrix. e) a model of normal dentin mineralization with high nucleation density and f) dentin mineralization in DSPP KO with low nucleation density. Red circles- the nucleation sites, yellow and purple concentric rings represent progression of dentin mineralization.tric rings represent progression of dentin minerali