Figure 4. KLFs in networks and signal integration.
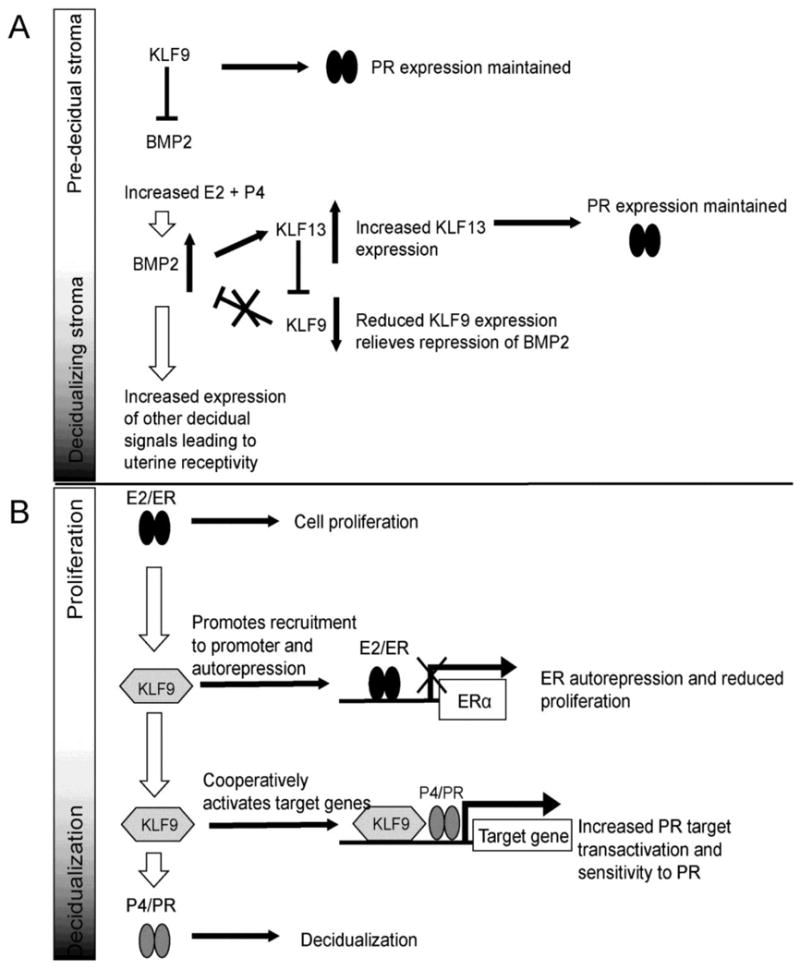
A) KLF9 and KLF913 have complementary and antagonist effects on uterine stromal cell decidualization. In the pre-implantation uterus KLF9 inhibits BMP2 expression. As P4 and E2 levels rise BMP2 expression is increased and leads to increased KLF13 expression. KLF13 repress KLF9 expression, relieving the block on BMP2 expression and further increasing the expression of decidualization signals. KLF9 upregulates PR in predecidual stroma and KLF13 upregulates PR in decidualizing stroma, which maintains cellular sensitivity to P4 across decidualization.. B) KLF9 integrates progesterone and estrogen signaling in the uterus. Estrogen leads to cell proliferation in the pre-decidual uterus. Elevated KLF9 levels promote ERα autorepression, which reduces cellular sensitivity to estrogen, thereby reducing endometrial proliferation and preparing the cell for P4 signaling. KLF9 also enhances PR transactivation, increasing the expression of P4/PR target genes and allowing decidualization to proceed. Filled arrows: direct activation or cause/effect relationship. Open arrows: sequential order of events. Abbreviations: PR, progesterone receptor; ER, estrogen receptor; BMP2, bone morphogenic protein 2; E2, estradiol; P4, progesterone.
