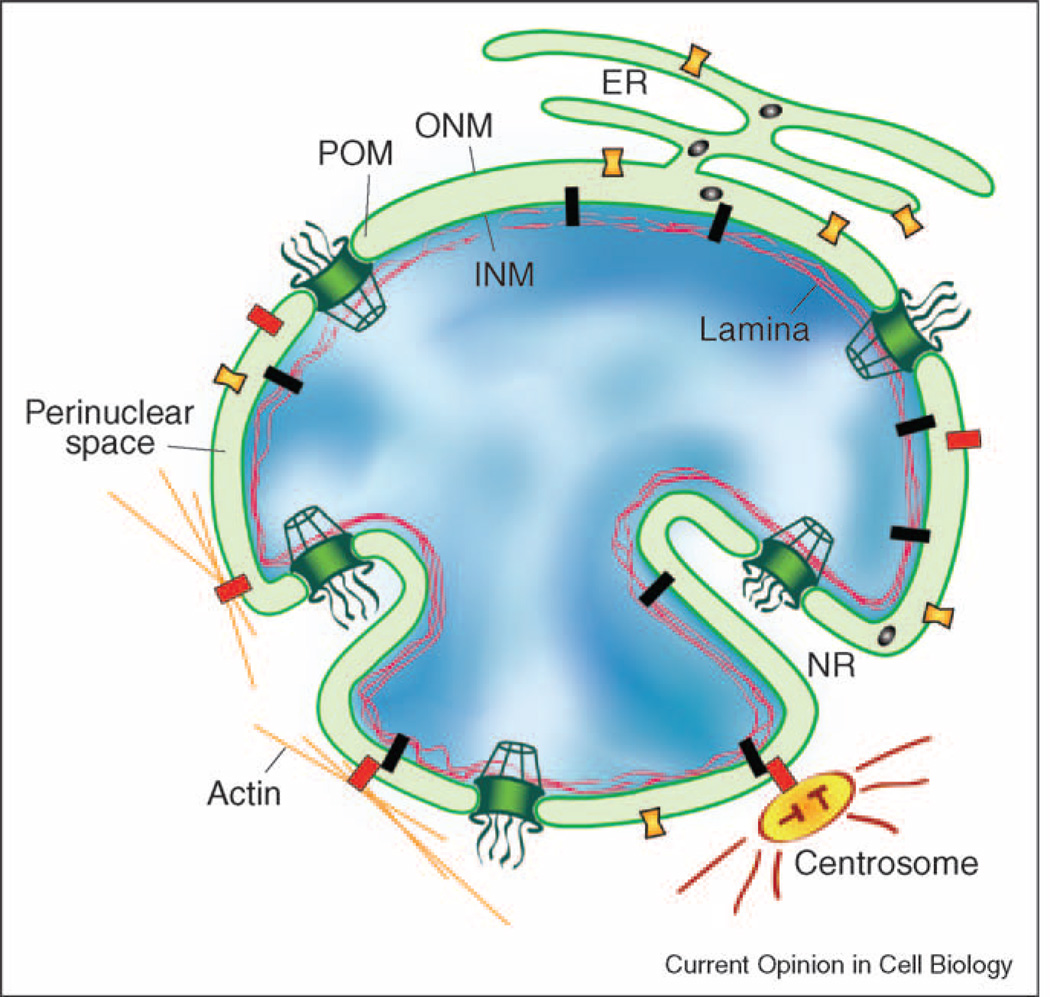
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the nucleus, highlighting membrane domains of the nuclear envelope (NE) and associated structures. The membrane system of the nuclear envelope consists of the outer nuclear membrane (ONM), the inner nuclear membrane (INM) and the pore membrane (POM). The ONM is contiguous with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Portions of the NE extend into the nucleus forming the nucleoplasmic reticulum (NR). The INM contains many distinct proteins (black) that contact the underlying lamina and chromatin. The pore membrane houses integral membrane proteins of nuclear pore complexes (green). Some ONM proteins (yellow) are also present within the ER and others (red) preferentially localize to the ONM and are proposed to bridge INM proteins to such cytoplasmic structures as the centrosome and actin filaments. Finally, another category of protein (blue ovals) is able to diffuse within the perinuclear space and to interact with luminal domains of NE proteins.