Figure 1. Microexon inclusion regulates protein–protein interactions in neurons.
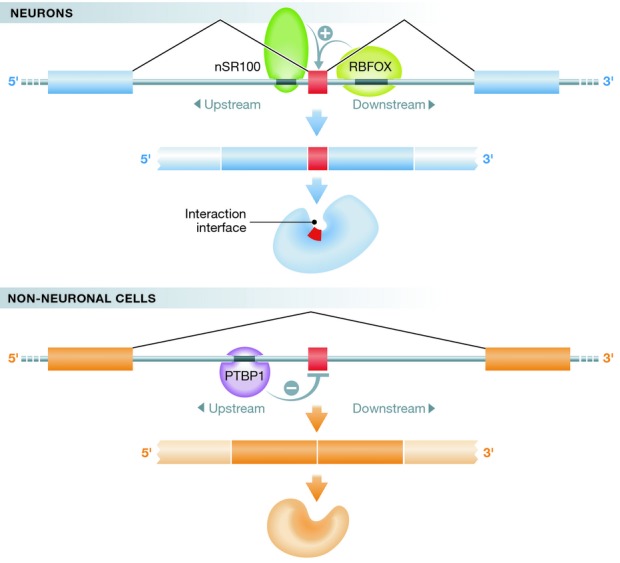
The regulation of microexons (shown in red) relies on RNA-binding proteins like nSR100, RBFOX, and PTBP1, which bind to conserved intronic flanks of microexons. nSR100 and RBFOX promote microexon inclusion in neurons, whereas PTBP1 seems to prevent microexon inclusion in non-neuronal cells. Microexons encode for domains important for protein–protein interactions, and their increased inclusion in neurons modulates protein interactions important for neuronal function.
