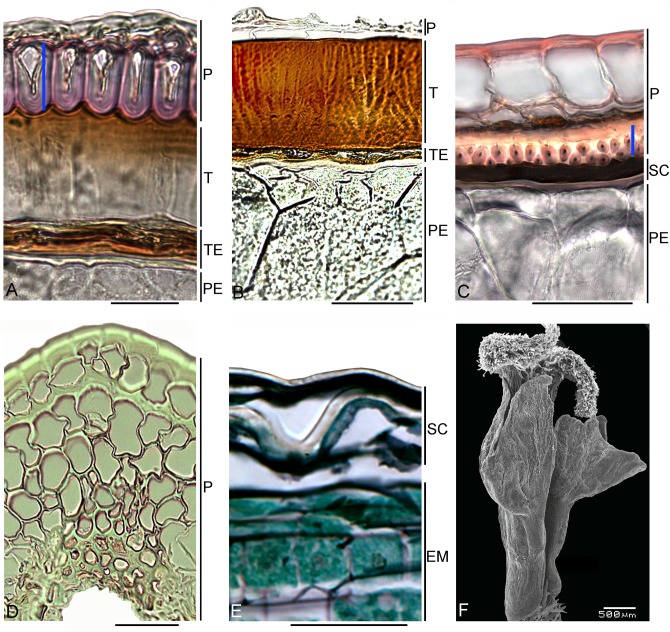
Fig 6. Carpology of the families Chenopodiaceae (A-E) and Sarcobataceae (F).
(A-E). Transverse sections. (A) Pericarp and seed coat of one of the dimorphic fruits of Axyris amaranthoides (Chenopodioideae-Axyrideae), vertical blue line indicates sclereid layer; cell cavities increase towards outside; crystals not present.(B) Fruit and seed of Chenopodium giganteum (Chenopodioideae-Chenopodieae). (C) Fruit and seed of Coryspermum sibiricum (Corispermoideae), vertical blue line indicates layer of sclereids. (D) Pericarp in the upper part of the fruit of Anabasis cretacea (Salsoloideae). (E) Seed coat of Anabasis cretacea. (F) SEM image of the young fruit of Sarcobatus baileyi forming radial wing. Abbreviations: EM—embryo, EN—endocarp, EX—exocarp, M—mesocarp, P—pericarp, PE—perisperm, SC—seed coat, T—testa, TE—tegmen. Bars = 10 μm (A), 50 μm (B-E), 500 μm (F).