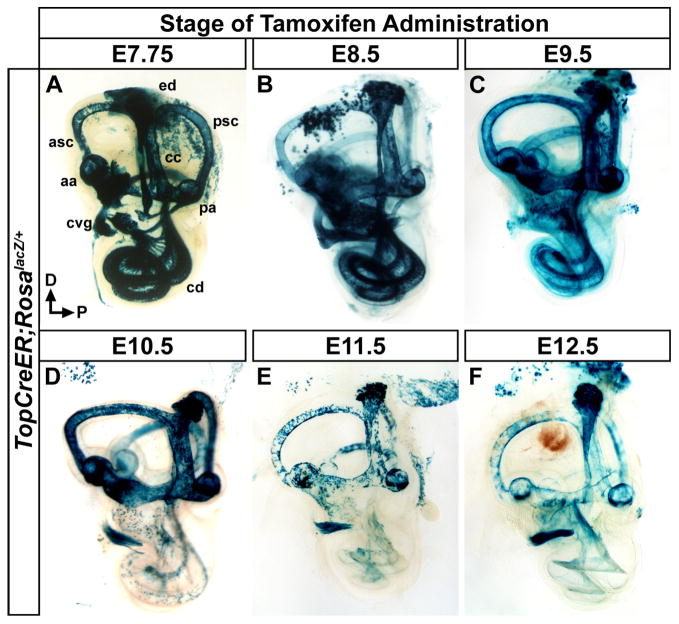
Figure 2. Temporal dynamics in the fate of Wnt responsive cells in the inner ear.
Whole mount views of X-gal stained inner ears (E18.5) exposed to tamoxifen at different developmental time points to induce TopCreER dependent activation of RosalacZ. (A–C) The inner ears of TopCreER; RosalacZ embryos receiving tamoxifen between E7.75 and E9.5 showed a high degree of X-gal staining in most dorsally derived vestibular structures including, the anterior and posterior semicircular canals (asc, psc) and associated ampullae (aa, pa), endolymphatic duct (ed), and common crus (cc). Ample staining was also observed in the ventrally derived cochlear duct (cd) and cochleovestibular ganglion (cvg). (D) Tamoxifen administration at E10.5 saw continued X-gal staining in vestibular structures, yet labeling in the cochlear duct was dramatically reduced. (E–F) TopCreER; RosalacZ embryos exposed to tamoxifen at E11.5 and E12.5 showed consistently patchy X-gal staining in vestibular structures due to reduced TopCreER expression at these stages. The cochlear duct was devoid of X-gal staining and sparse labeling was observed in the spiral ganglia.