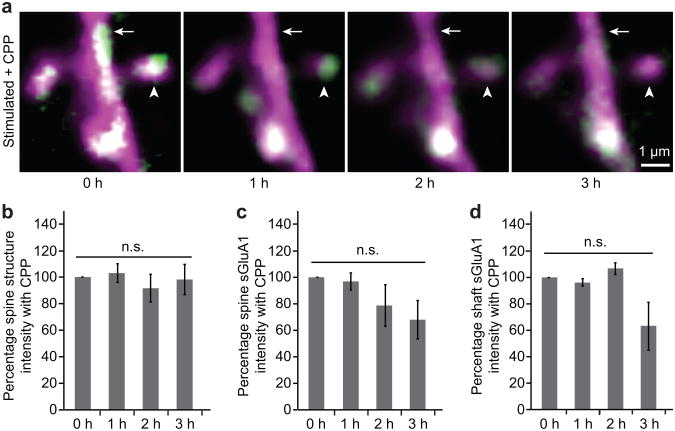
Figure 5. Increase in spine sGluA1 following whisker stimulation is NMDA receptor dependent.
a, Representative images of dendrites taken before (0 hour) and after (hour 1, 2, 3) acute whisker stimulation in animals with CPP treatment. Arrowheads mark spines and arrows mark dendritic shafts (SEP-GluA1 in green, dsRed2 in magenta, overlap in white). b, Spine structure intensity following whisker stimulation with CPP treatment. c, Spine sGluA1 intensity following whisker stimulation with CPP treatment. d, Shaft sGluA1 intensity following whisker stimulation with CPP treatment. 30 spines, 5 dendrites in 2 animals for CPP treatments. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttests. Error bars = s.e.m.