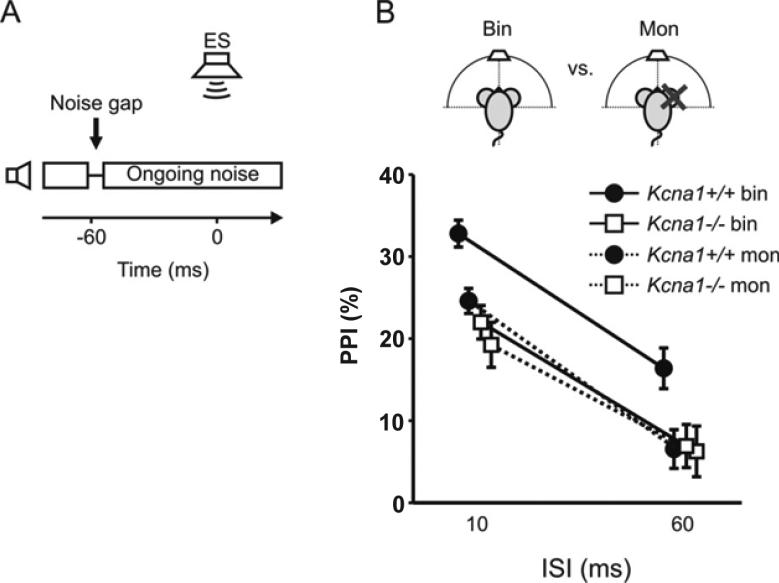
Figure 4. Kcna1+/+ mice but not Kcna1−/− mice benefit from binaural hearing in gap detection tasks.
A) Stimulus condition showing the offset and onset of otherwise ongoing noise presented by one speaker to produce a 10 ms gap starting 60 ms before the ES at time point 0 s. B) PPI scores for the Kcna1+/+ (circles, n=19) and the Kcna1−/− mice (squares, n=12) with binaural (solid lines) and monaural listening (dashed lines, cartoon) for ISIs between noise offset and ES of 10 ms (left) and 60 ms (right). All data are given as Mean (±SEM).