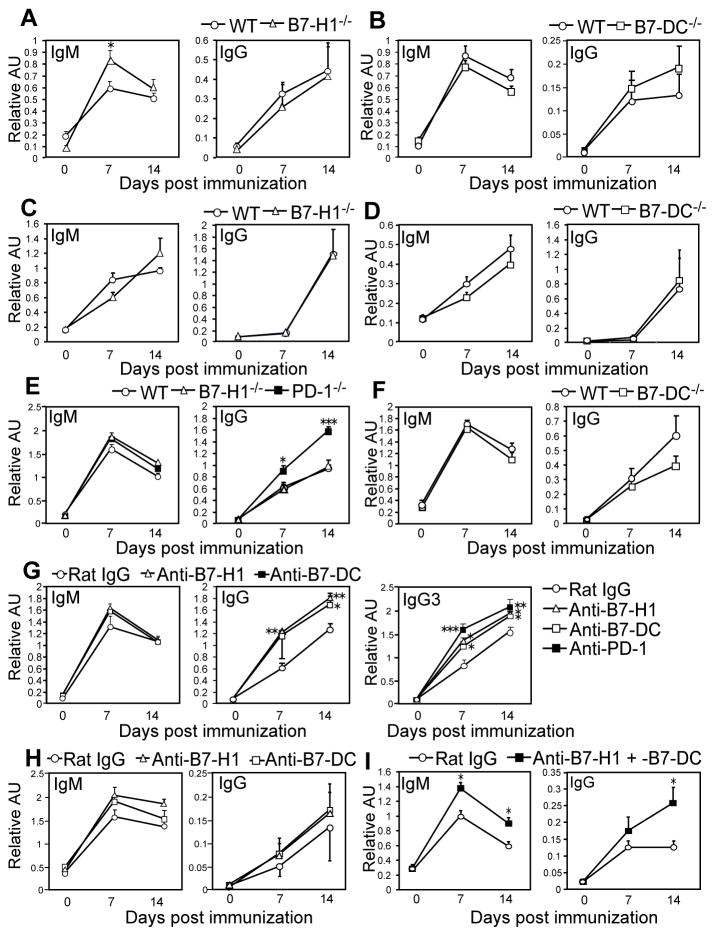
Figure 6. B7-H1 and B7-DC are both required for suppression of PPS-specific IgG responses.
A–B) PPS3-specific serum IgM and IgG levels in B7-H1−/− (A) and B7-DC−/− (B) mice 0, 7, and 14 days post PPV23 immunization (~0.1 μg PPS3) relative to WT mice. C–D) PPS3-specific serum IgM and IgG levels in B7-H1−/− (C) and B7-DC−/− (D) mice following immunization with Prevnar-13 (~0.1 μg PPS3). E–F) TNP-specific serum IgM and IgG levels in WT, PD-1−/−, B7-H1−/−, and B7-DC−/− mice following TNP-Ficoll immunization. G) TNP-specific serum IgM, IgG, and IgG3 levels in WT mice administered blocking mAbs against B7-H1, B7-DC, PD-1 or rat IgG control mAbs following TNP-Ficoll immunization. H–I) PPS3-specific IgM and IgG levels in WT mice administered single blocking mAbs against B7-H1 or B7-DC (H) or blocking mAbs against both B7-H1 and B7-DC (I) following PPV23 immunization. A–I) Mean values (± SEM; n ≥4 mice/group) are shown. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences in values between knockout mice and WT mice (A and E) or WT mice receiving control mAbs and functional PD-1/PDL blocking mAbs (G and I) (p ≤ 0.05, *; p ≤0.01, **; p ≤0.001, ***; unpaired Student’s t test).