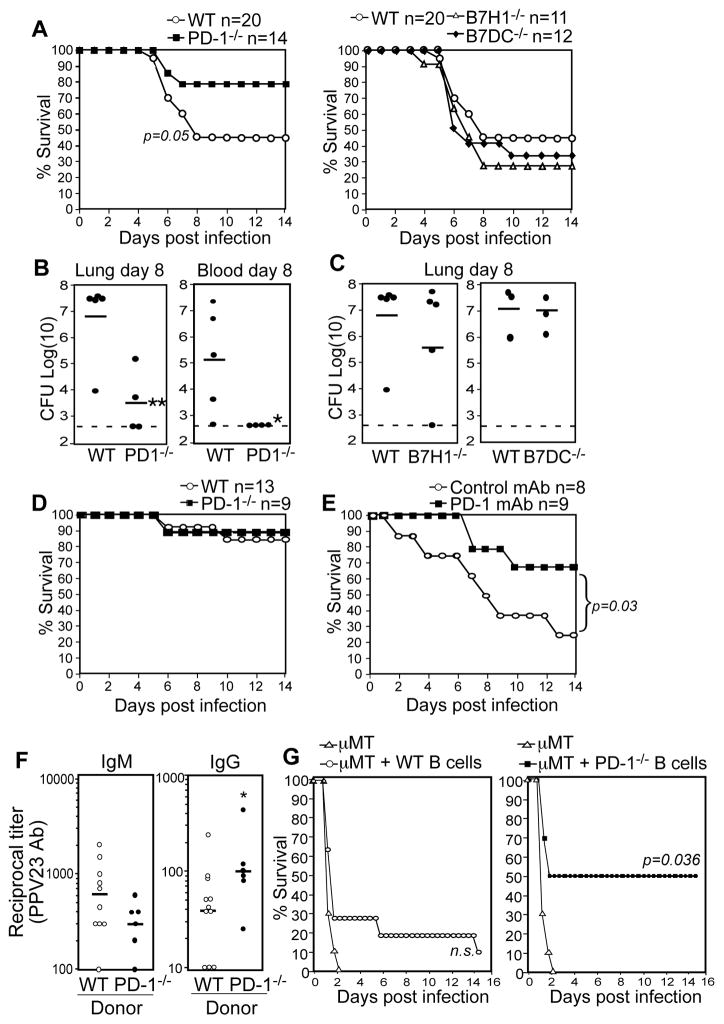
Figure 7. PPS immunization in the context of PD-1 deficiency or blockade significantly increases survival against lethal respiratory S. pneumoniae infection and is dependent on B cell-intrinsic PD-1 expression.
A–C) Purified PPS3-immunized WT, PD-1−/−, B7-H1−/−, and B7-DC−/− mice were challenged with a lethal i.n. dose (1 × 107 CFU) of WU2 28 days following immunization. A–B) Survival analysis shows a significant difference between PD-1−/− and WT mice (p=0.05; Fisher’s Exact test). B–C) Total lung (B and C) and blood (per mL; B only) CFU 8 days post challenge. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences in CFU between WT and PD-1−/− mice (p ≤0.05, *; p ≤ 0.01, **; Student’s t test). D) Survival in Prevnar-13-immunized WT and PD-1−/− mice challenged i.n. with 107 CFU WU2 28 days following immunization. E) Survival in WT mice given PD-1 blocking or control mAbs at the time of purified PPS3 immunization (as described in Fig. 6 legend) and challenged i.n. with 1 × 107 CFU WU2 28 days following immunization (n=8–9 mice/group). Survival curves were significantly different as determined by Log-rank analysis (p=0.03). F–G) Reconstitution of μMT mice with B cells from PD-1−/− mice yields significantly increased PPS-specific IgG responses and significantly increases protection against infection. Control μMT mice (n=10), and μMT mice reconstituted with 2 × 107 wild type (n=11) or PD-1−/− (n=6) spleen B cells, were immunized on d1 as in Figure 4. F) PPV23-specific IgM and IgG reciprocal endpoint dilution titers were determined for d7 sera and were defined as the dilution yielding an OD405nm value 3-fold higher than values for non-reconstituted μMT mice. (*p=0.04, unpaired Student’s t test). G) Mice were infected i.p. with 200 CFU WU2 on d8, with differences in overall survival assessed by Fisher’s Exact test.