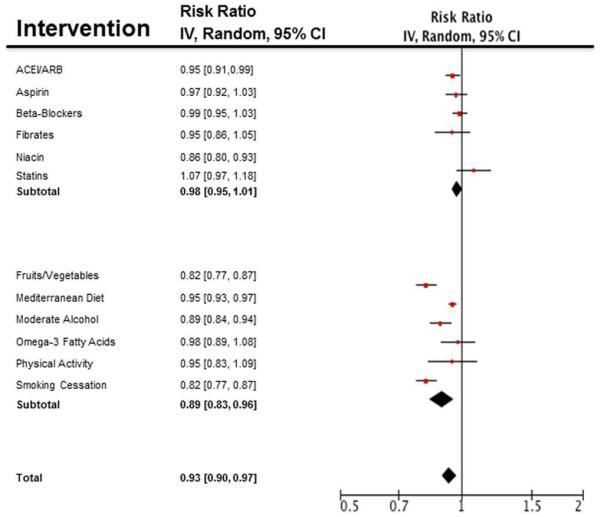
Figure 1.
Estimates of risk ratio reduction based on recent meta-analyses of trials examining medication adherence vs. placebo and lifestyle interventions vs. control. Estimates on the effect of niacin were removed as there are no recent meta-analyses which include recent negative data. Relative risks are reported with logarithmic conversions and standard errors plotted on the Forest plot. Estimates of lifestyle modifications such as the Mediterranean diet as a whole (106), fruits and vegetables (59, 61, 62), smoking cessation (103), moderate alcohol (105), omega-3 fatty acids (110), and improved physical activity (102) have substantial benefits for CVD prevention not seen with commonly used standard medical therapies such as statins (100, 101), renin-angiotensin system blockade (104), Fibrates (107), aspirin (108), beta-blockers (109),