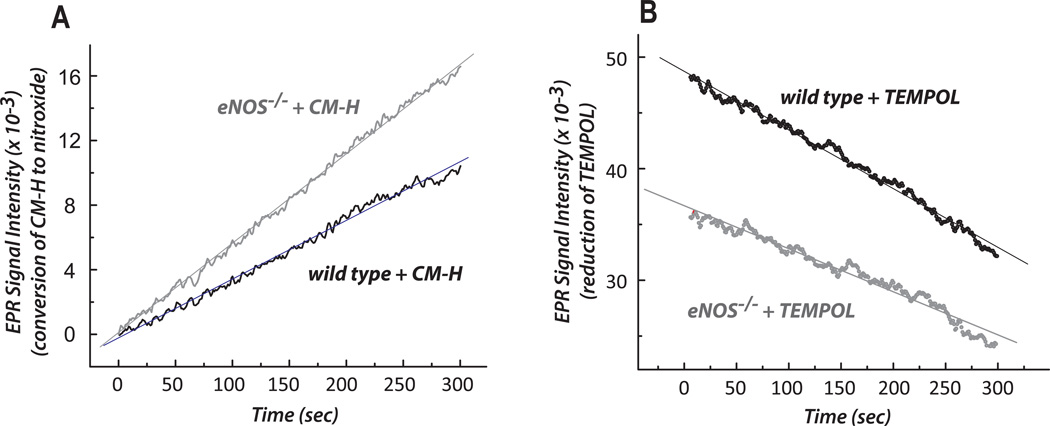
Fig. 3. The redox activities of the myocardium from wild type and eNOS−/− were measured by EPR with the spin probes of CM-H (in A) and TEMPOL (in B).
Conversion of CM-H to stable nitroxide was measured by EPR at 298K in tissue homogenates (0.25 mg/mL) of wild type or eNOS−/− myocardium in SHE buffer (250 mM sucrose, 10 mM HEPES, and 1 mM EDTA, pH 7.4) containing 1 mM DTPA and 1 mM CM-H (in A) or TEMPOL (in B). The instrumental settings used for detecting the three-line spectrum of the nitroxide formed were: center field, 3360.3 G; sweep width, 60 G; microwave frequency, 9.43 GHz; power, 20 mW; receiver gain, 5.02 × 103; modulation frequency, 100kHz; modulation amplitude, 1 G; time constant, 163.84 ms; conversion time, 41 ms; sweep time, 42 sec; number of X-scans, 1. The parameters for the kinetic mode were: static field, 3360.3 G; receiver gain, 2 × 103; time constant, 2624.44 ms; conversion time, 1,000 ms; and sweep time, 300s; number of scans, 1. The CM-H oxidation experiment was performed three times (n=3) for calculating redox activity.