Fig. 1.
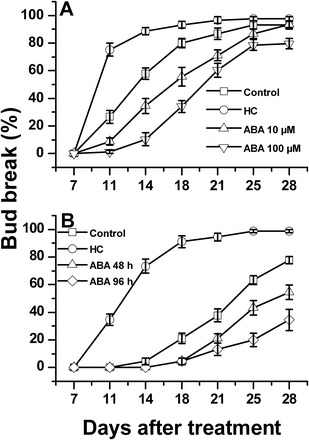
ABA delays bud break in a concentration- and duration-dependent manner. Vines of Vitis vinifera cv. Early Sweet from a vineyard at Gilgal, located in the Jordan Valley, were pruned to three-node spurs. The detached canes were cut into single-node cuttings, randomly mixed, and groups of 10 cuttings were prepared. (A) Four treatments were carried out, each with nine groups of 10 cuttings. The bases of the cuttings were immersed in vases containing 10 μM ABA, 100 μM ABA (with 0.02% Triton), or only 0.02% Triton (for control and HC treatments). The vases were placed in a growth chamber and forced at 22 °C under a 14h/10h light/dark regime. After 48h, the solutions were replaced with tap water, and sprayed with 0.02% Triton instead, apart from the HC-treated buds which were sprayed with 3% ‘Dormex’ as detailed in the Materials and methods. The treated groups were forced under the above conditions for another 28 d. Bud break was monitored at 7, 11, 14, 18, 21, 25, and 28 d after spraying. Values are averages of the nine groups in each treatment ±SE. (B) Both ABA treatments were carried out using 100 μM ABA. In the ABA 96h treatment, the cuttings were returned to ABA solution for an additional 48h after spraying. All other details are as in (A).
