Figure 2. Cumulative incidence of strabismus among premature infants.
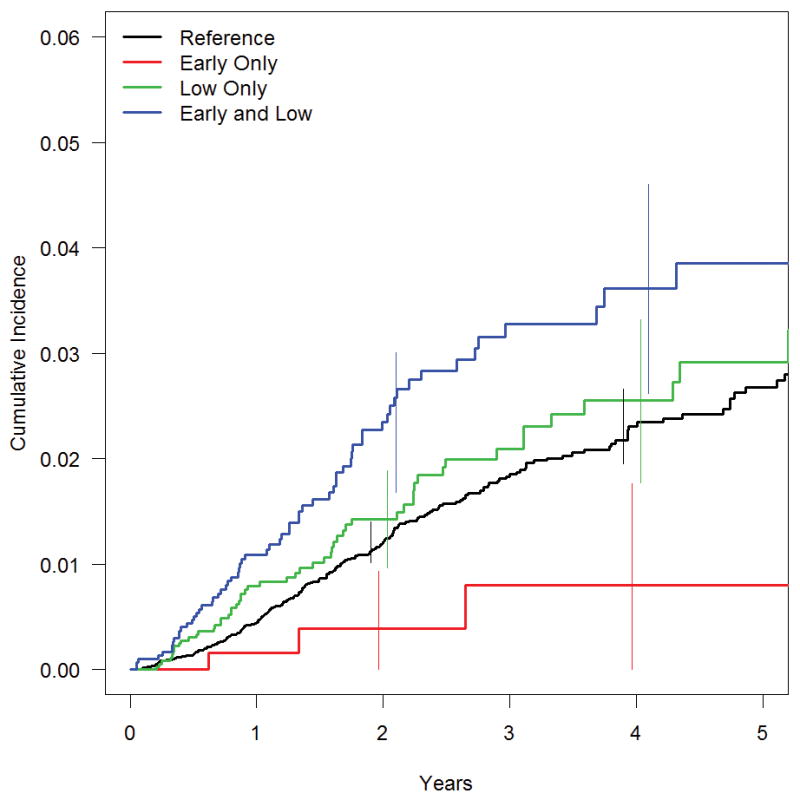
The cumulative incidence of strabismus estimated by Kaplan-Meier for all study participants and for infants in four primary exposure groups: Very low birth weight, very premature (LBW, VP; n=2980), Very low birth weight, mildly premature (LBW, MP; n=3591), Mildly low birth weight, mildly premature (MLBW, MP; n=18365), and Mildly low birth weight, very premature (MLBW, VP; n=665). 95% confidence intervals for each exposure group are shown at two and at four years. The effect of birth weight (low birth weight increases incidence of strabismus) is consistent across different levels of gestational age; the effect of gestational age is not.
